-
History and Origin of Maritime Law: A Comprehensive Guide for Curious Readers
- The Birth of Maritime Law: A Journey into Ancient Times
- The Middle Ages: Expansion and Codification
- The Rise of Maritime Empires: Shaping the Global Landscape
- The 19th and 20th Centuries: Modernization and International Cooperation
- Modern Maritime Law: A Complex Web of Regulations
- Table: Key International Maritime Law Conventions
- Conclusion: A Legacy of Maritime Law
-
FAQ about History and Origin of Maritime Law
- 1. What is maritime law?
- 2. When did maritime law originate?
- 3. What is the Rhodian Sea Law?
- 4. What role did the Romans play in maritime law?
- 5. What is the "Law of the Sea"?
- 6. How did the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) impact maritime law?
- 7. What is the International Maritime Organization (IMO)?
- 8. What are some common areas covered by maritime law?
- 9. How are maritime disputes resolved?
- 10. What is the future of maritime law?
History and Origin of Maritime Law: A Comprehensive Guide for Curious Readers

Welcome, curious readers! Today, we embark on an exciting journey to explore the history and origin of maritime law, a fascinating realm that has shaped the course of human civilization. We’ll dive into the past to uncover its ancient roots and trace its evolution through the centuries. Along the way, we’ll unravel the intricate regulations and social norms that have governed the vast expanse of our oceans and waterways. So, buckle up for a thrilling adventure into the world of maritime law!
The Birth of Maritime Law: A Journey into Ancient Times
Maritime law has its humble beginnings in the distant past, when humans first ventured out into the open seas. As seafaring became increasingly prevalent, the need arose for a common set of rules and regulations to maintain order and ensure fairness among traders and sailors. One of the earliest known codes of maritime law is the Rhodian Sea Law, a comprehensive document dating back to the 7th century BC. This code established guidelines for maritime trade, including contracts, insurance, and dispute resolution.
Over time, as sea trade flourished in the Mediterranean and beyond, other civilizations developed their own maritime laws. The Greeks, for instance, enacted the Athenian Maritime Code in the 5th century BC, which dealt with issues of piracy, crew contracts, and admiralty jurisdiction. Similarly, the Romans established a robust set of maritime laws under the Lex Rhodia de Jactu, which provided a framework for addressing shipwrecks and cargo losses.
The Middle Ages: Expansion and Codification
The Middle Ages witnessed a surge in maritime commerce and exploration, giving rise to new challenges and a need for more comprehensive maritime laws. During this period, several significant legal documents emerged, including the infamous "Rôles d’Oléron" (12th century), the "Consolato del Mare" (14th century), and the "Laws of Wisby" (13th century). These documents codified existing maritime customs and practices, providing greater clarity and uniformity in the application of maritime law.
The Rise of Maritime Empires: Shaping the Global Landscape
As European nations began to establish their maritime empires in the 15th and 16th centuries, they sought to enforce their own maritime laws upon the vast oceans they traversed. Spain, Portugal, France, and England all enacted their own comprehensive codes of maritime law, often drawing inspiration from earlier sources such as the Rhodian Sea Law. These laws covered a wide range of topics, including ship registration, admiralty courts, and privateering.
The maritime laws of this era played a pivotal role in shaping the global trade landscape. As European powers asserted their dominance over the seas, they imposed their maritime regulations on their colonies and trading partners, gradually creating a more standardized and internationalized maritime legal system.
The 19th and 20th Centuries: Modernization and International Cooperation
The 19th and 20th centuries brought about unprecedented advancements in maritime technology and communication, leading to a renewed need for international cooperation in maritime law. In 1921, the League of Nations established a "Maritime Safety Committee" to address emerging challenges, such as the safety of navigation and the prevention of marine pollution. This committee became the forerunner of the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which was founded in 1948 and remains the primary international body responsible for developing and enforcing maritime regulations.
Modern Maritime Law: A Complex Web of Regulations
Today, the body of maritime law is a complex and multifaceted system that encompasses a vast array of subjects. It includes laws governing ship registration, cargo transportation, crew welfare, maritime insurance, maritime safety, and environmental protection. Maritime law also plays a vital role in regulating activities such as fishing, offshore oil and gas exploration, and marine scientific research.
Table: Key International Maritime Law Conventions
| Convention | Purpose | Year of Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Convention on the High Seas | Codified international law for the high seas | 1958 |
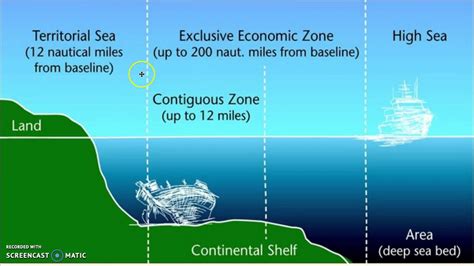
| Convention on the Territorial Sea and the Contiguous Zone | Defined the breadth of territorial seas and established rules for the contiguous zone | 1958 |
| Convention on the Continental Shelf | Established the legal framework for the exploration and exploitation of underwater natural resources | 1958 |
| International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) | Aimed to prevent pollution of the marine environment by ships | 1973 |
| United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) | A comprehensive framework for all aspects of the law of the sea | 1982 |
Conclusion: A Legacy of Maritime Law
The history and origin of maritime law is a captivating tale of human ingenuity, innovation, and cooperation. From the ancient Rhodian Sea Law to the modern United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, maritime law has evolved alongside the development of our globalized world. Today, it stands as a testament to the critical importance of regulating and maintaining order in the vast and interconnected realm of the oceans.
Readers, we encourage you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of maritime law. Explore the resources below to learn more about this essential aspect of international law:
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- American Bar Association: Maritime Law Committee
FAQ about History and Origin of Maritime Law
1. What is maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law is a legal framework that governs maritime issues such as shipping, navigation, trade, and safety.
2. When did maritime law originate?
Answer: Maritime law’s origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Phoenicia, Greece, and Rome.
3. What is the Rhodian Sea Law?
Answer: The Rhodian Sea Law was a code of maritime law developed by the Rhodians in the 9th century BC. It established rules for navigation, contracts, and cargo.
4. What role did the Romans play in maritime law?
Answer: The Romans adopted and expanded the Rhodian Sea Law into their own legal system, which greatly influenced modern maritime law.
5. What is the "Law of the Sea"?
Answer: The "Law of the Sea" refers to the body of international law that governs activities on the world’s oceans.
6. How did the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) impact maritime law?
Answer: UNCLOS established a comprehensive framework for maritime law, covering territorial waters, sea zones, the environment, and other issues.
7. What is the International Maritime Organization (IMO)?
Answer: The IMO is a specialized agency of the UN responsible for developing and implementing international maritime regulations.
8. What are some common areas covered by maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law includes topics such as vessel registration, maritime contracts, liability for accidents, pollution prevention, and passenger rights.
9. How are maritime disputes resolved?
Answer: Maritime disputes can be resolved through arbitration, international tribunals, or national courts.
10. What is the future of maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law continues to evolve to address new challenges, such as marine environmental protection, cybersecurity, and autonomous shipping.