- Introduction
- Federal Maritime Laws: A Historical Voyage
- Regulating Maritime Commerce
- International Maritime Conventions
- Environmental Protection
- Enforcement and Remedies
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about Federal Maritime Laws
- What are federal maritime laws?
- Who enforces federal maritime laws?
- What are some of the most important federal maritime laws?
- How do federal maritime laws affect the maritime industry?
- How can I learn more about federal maritime laws?
- What are the penalties for violating federal maritime laws?
- How can I report a violation of federal maritime laws?
- What are some of the challenges to enforcing federal maritime laws?
- What are the future trends in federal maritime laws?

Introduction
Ahoy, readers! Welcome aboard our comprehensive exploration of federal maritime laws. This guide will navigate you through the vast waters of maritime regulations, ensuring you understand the rules that govern the high seas. Whether you’re a seasoned seafarer or a newbie dipping your toes into maritime matters, we’ve got you covered. So, fasten your life vests and prepare for an enlightening journey!
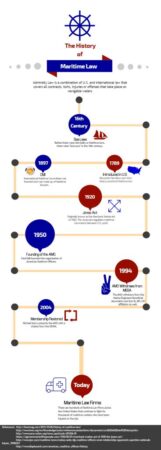
Federal Maritime Laws: A Historical Voyage
Maritime laws have a long and storied history, dating back to ancient times. As seafaring nations expanded their reach, a need arose for clear rules to govern maritime conduct. The United States is no exception. Federal maritime laws in the US trace their origins to the early days of the Republic. Over time, these laws have evolved significantly, adapting to the changing needs of the maritime industry.
The Admiralty Jurisdiction Act
One of the foundational maritime laws in the US is the Admiralty Jurisdiction Act of 1789. This act established federal jurisdiction over maritime cases. It defined maritime jurisdiction as "any navigable waterway connected to the sea." This definition has been interpreted broadly over the years and now includes most inland waterways and even some non-navigable waters used in interstate or foreign commerce.
Regulating Maritime Commerce
The Merchant Marine Act of 1920
The Merchant Marine Act of 1920, also known as the Jones Act, is another important piece of federal maritime law. The Jones Act imposes strict liability on vessel owners for injuries sustained by seamen in the course of their employment. This law has been interpreted to provide extensive protection for seamen, including a right to maintenance and cure, and damages for pain and suffering.
The Federal Maritime Commission Act
The Federal Maritime Commission Act of 1961 created the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC). The FMC is an independent agency that regulates the shipping industry. The FMC’s responsibilities include regulating rates, practices, and agreements among ocean carriers and marine terminal operators. The FMC also investigates and prosecutes violations of federal maritime laws.
International Maritime Conventions
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS)
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is a comprehensive treaty that sets out minimum safety standards for ships operating at sea. SOLAS covers a wide range of topics, including ship design, construction, and equipment, as well as crew training and safety management.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO)
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that oversees the development and implementation of global maritime regulations. The IMO is responsible for the development of SOLAS and other important maritime conventions.
Environmental Protection
The Clean Water Act
The Clean Water Act (CWA) regulates discharges of pollutants into navigable waters. The CWA has been interpreted to apply to discharges from vessels, including oil spills and other hazardous substances. The CWA also regulates the discharge of ballast water from ships, which can introduce invasive species into new ecosystems.
The Oil Pollution Act of 1990
The Oil Pollution Act of 1990 (OPA) was enacted in response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. OPA establishes a comprehensive framework for preventing and responding to oil spills. The act imposes strict liability on vessel owners and operators for oil spills, and it creates a fund to compensate victims of oil spills.
Enforcement and Remedies
The Coast Guard
The Coast Guard is responsible for enforcing federal maritime laws. The Coast Guard has a variety of enforcement tools at its disposal, including inspections, citations, and arrests. The Coast Guard also investigates maritime accidents and casualties.
Civil and Criminal Penalties
Violations of federal maritime laws can result in both civil and criminal penalties. Civil penalties can include fines, injunctions, and other remedies. Criminal penalties can include imprisonment.
Conclusion
There you have it, readers! This comprehensive guide has shed light on the fascinating world of federal maritime laws. We encourage you to explore our other articles for further insights into this complex and ever-evolving field. Stay tuned for more maritime adventures, where the law meets the open sea!
Related Articles:
- [A Deep Dive into Admiralty Law: Understanding the Rules of the Sea](link to article)
- [Navigating the Legal Seas: A Guide to Maritime Contracts](link to article)
- [Unveiling the Secrets of Maritime Insurance: A Safety Net for Sailors](link to article)
FAQ about Federal Maritime Laws
What are federal maritime laws?
Answer: Federal maritime laws are a body of laws that govern maritime activities within the jurisdiction of the United States. They cover a wide range of topics, including navigation, safety, pollution prevention, and maritime commerce.
Who enforces federal maritime laws?
Answer: The U.S. Coast Guard is responsible for enforcing federal maritime laws. The Coast Guard has a variety of resources at its disposal, including ships, aircraft, and personnel, to carry out its mission.
What are some of the most important federal maritime laws?
Answer: Some of the most important federal maritime laws include the Jones Act, the Limitation of Liability Act, and the Oil Pollution Act. These laws protect the rights of seamen, limit the liability of shipowners, and prevent pollution of the marine environment.
How do federal maritime laws affect the maritime industry?
Answer: Federal maritime laws have a significant impact on the maritime industry. These laws help to ensure the safety of mariners, protect the marine environment, and promote fair competition in the maritime marketplace.
How can I learn more about federal maritime laws?
Answer: There are a number of resources available to help you learn more about federal maritime laws. You can find information on the websites of the U.S. Coast Guard, the Maritime Administration, and the National Transportation Safety Board. You can also find information in books, articles, and legal databases.
What are the penalties for violating federal maritime laws?
Answer: The penalties for violating federal maritime laws can be severe. Violators may face fines, imprisonment, or both. In some cases, violators may also be held liable for damages caused by their actions.
How can I report a violation of federal maritime laws?
Answer: If you witness a violation of federal maritime laws, you can report it to the U.S. Coast Guard. You can call the Coast Guard’s National Response Center at 1-800-424-8802, or you can file a report online at www.uscg.mil/nrc.
What are some of the challenges to enforcing federal maritime laws?
Answer: Enforcing federal maritime laws can be challenging due to the vastness of the ocean and the difficulty of monitoring maritime activities. However, the U.S. Coast Guard is committed to enforcing these laws and protecting the safety of mariners and the marine environment.
What are the future trends in federal maritime laws?
Answer: The future of federal maritime laws is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including the increasing use of technology in maritime operations, the growth of global trade, and the need to protect the marine environment.