- Exxon Fed Maritime Law: A Comprehensive Guide
-
FAQ about Exxon Fed Maritime Law
- Q: What is the Exxon Fed Maritime Law?
- Q: What does the law cover?
- Q: What are the key provisions of the law?
- Q: Who is liable for oil spills?
- Q: What are the penalties for violating the law?
- Q: How has the law been implemented?
- Q: What is the National Oil and Hazardous Substances Pollution Contingency Plan (NCP)?
- Q: What is the Oil Pollution Act of 1990 (OPA)?
- Q: How has the law affected the maritime industry?
- Q: What are the future challenges of the law?
Exxon Fed Maritime Law: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Greetings, readers! Today, we delve into the complexities and implications of "exxon fed maritime law." As we navigate this legal landscape together, we’ll explore its origins, key provisions, and the impact it has on various stakeholders in the maritime industry. So buckle in and let’s set sail into the world of maritime law.
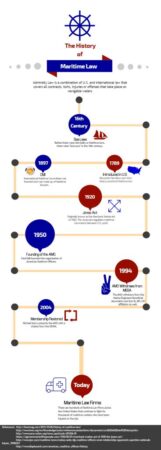
Historical Origins of Exxon Fed Maritime Law
The roots of Exxon Fed maritime law can be traced back to the Exxon Valdez oil spill in 1989. This catastrophic event, which resulted in a massive oil leak into the pristine waters of Alaska’s Prince William Sound, sparked outrage and prompted a comprehensive review of existing maritime regulations. Following the spill, Congress passed the Oil Pollution Act of 1990, better known as "OPA 90," which established strict liability and financial responsibility for oil spills and other maritime casualties.
Key Provisions of Exxon Fed Maritime Law
OPA 90 provides a robust framework for addressing oil spills and other maritime incidents in U.S. waters. Its key provisions include:
Liability and Compensation
OPA 90 imposes strict liability on vessels and their owners for oil spills. This means that the owner or operator of a vessel is responsible for cleanup costs and damages, regardless of fault or negligence. The law also establishes a compensation fund to cover claims from victims of oil spills.
Vessel Safety and Prevention
OPA 90 mandates various safety measures for vessels carrying oil, including double hulls, state-of-the-art navigation systems, and spill prevention equipment. The law also authorizes the Coast Guard to inspect vessels and enforce safety regulations.
Impact of Exxon Fed Maritime Law
The passage of Exxon Fed maritime law has had a profound impact on the maritime industry, including:
Enhanced Safety Measures
The safety provisions of OPA 90 have led to significant improvements in the safety of U.S. vessels and the prevention of oil spills. Double hulls, improved navigation systems, and enhanced spill response capabilities have all contributed to a reduction in maritime accidents and their associated environmental damage.
Increased Financial Responsibility
The strict liability provisions of OPA 90 have made vessel owners and operators more financially responsible for oil spills and other maritime incidents. This has led to a greater emphasis on safety and risk management within the industry.
Legal Challenges and Case Studies
Despite its comprehensive nature, Exxon Fed maritime law has faced legal challenges and been the subject of various case studies. Some significant legal cases involving OPA 90 include:
In re Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Litigation (1994)
This landmark case involved the Exxon Valdez oil spill and resulted in a $5 billion settlement, demonstrating the potential liability under OPA 90.
United States v. Atlantic Richfield Company (2000)
This case upheld the strict liability provisions of OPA 90, affirming the principle that vessel owners are responsible for damages regardless of fault.
Comparative Analysis with International Law
Exxon Fed maritime law shares similarities with international maritime laws, such as the International Convention on Oil Pollution Preparedness, Response, and Cooperation (OPRC), 1990. However, there are also key differences, such as the strict liability and compensation fund provisions in OPA 90.
Table of Key Provisions
| Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Strict Liability | Vessels are responsible for oil spills regardless of fault |
| Compensation Fund | Fund to cover claims from victims of oil spills |
| Double Hulls | Required on vessels carrying oil |
| State-of-the-Art Navigation Systems | Required on vessels carrying oil |
| Spill Prevention Equipment | Required on vessels carrying oil |
Conclusion
Exxon Fed maritime law is a complex and multifaceted body of law that has significantly impacted the maritime industry. From its origins in the Exxon Valdez oil spill to its ongoing evolution through legal challenges and case studies, this law serves as a crucial framework for protecting marine environments and ensuring financial responsibility in the event of maritime incidents.
We invite you to explore other articles on our website for further insights into the world of maritime law. Thank you for joining us on this legal journey!
FAQ about Exxon Fed Maritime Law
Q: What is the Exxon Fed Maritime Law?
A: This law is a federal law in the United States that governs the maritime industry. It was enacted in 1990 in response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill.
Q: What does the law cover?
A: The law covers a wide range of maritime issues, including oil spills, vessel safety, and marine environmental protection.
Q: What are the key provisions of the law?
A: The law includes provisions that establish liability for oil spills, require vessels to carry insurance, and set standards for vessel safety.
Q: Who is liable for oil spills?
A: The vessel owner is generally liable for oil spills. However, there are exceptions to this rule, such as if the spill was caused by an act of war or natural disaster.
Q: What are the penalties for violating the law?
A: Penalties for violating the law can include fines, imprisonment, and the loss of a vessel’s license.
Q: How has the law been implemented?
A: The law has been implemented through a variety of regulations and programs. These include the National Oil and Hazardous Substances Pollution Contingency Plan (NCP) and the Oil Pollution Act of 1990 (OPA).
Q: What is the National Oil and Hazardous Substances Pollution Contingency Plan (NCP)?
A: The NCP is a federal plan that describes how the government will respond to oil and hazardous substance spills.
Q: What is the Oil Pollution Act of 1990 (OPA)?
A: The OPA is a federal law that strengthens the government’s ability to prevent and respond to oil spills.
Q: How has the law affected the maritime industry?
A: The law has had a significant impact on the maritime industry. It has led to increased safety standards, improved oil spill response capabilities, and greater financial responsibility for vessel owners.
Q: What are the future challenges of the law?
A: The future challenges of the law include addressing the increasing risk of oil spills from offshore drilling and the need to strengthen international cooperation on maritime safety.