- The Law of the Water Maritime: A Comprehensive Guide
- Admiralty Law: The Origins and Evolution
- Jurisdiction and Territorial Waters
- The Law of the Sea and International Conventions
- Maritime Contracts and Disputes
- The Future of Maritime Law
- Table: Key Concepts in the Law of the Water Maritime
- Conclusion
-
FAQ About Law of the Water Maritime
- What is the Law of the Water Maritime?
- What are the main principles of the Law of the Water Maritime?
- What is the history of the Law of the Water Maritime?
- What are the different types of maritime law?
- What are the key legal issues in maritime law?
- What are the main sources of maritime law?
- How is maritime law enforced?
- What are the latest developments in maritime law?
- What are the challenges facing maritime law?
- What is the future of maritime law?
The Law of the Water Maritime: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Greetings, readers! Welcome to our in-depth exploration of the law of the water maritime, a fascinating and complex field that governs the vast expanse of the world’s oceans and waterways. Whether you’re a maritime professional, an enthusiast of nautical adventures, or simply curious about this intriguing legal domain, we invite you to join us on this journey into the depths of maritime law.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various aspects of the law of the water maritime, encompassing everything from the historical origins of maritime law to the latest developments in international conventions and regulations. We’ll navigate through the complexities of territorial waters, jurisdiction, maritime boundaries, and so much more. Along the way, we’ll uncover the stories and principles that shape this dynamic and ever-evolving legal landscape. So, sit back, relax, and prepare to set sail on an adventure into the uncharted waters of maritime law.
Admiralty Law: The Origins and Evolution
The Birth of Maritime Law
The law of the water maritime has its roots in ancient times, when maritime trade and exploration thrived along the bustling shores of the Mediterranean Sea. As seafaring nations emerged, the need for laws to govern their interactions at sea became increasingly apparent. By the Middle Ages, a comprehensive body of maritime law had developed, known as admiralty law. Admiralty law initially focused on regulating maritime commerce, including issues of contracts, cargo disputes, and piracy.
The Rise of International Maritime Law
Over time, as maritime trade expanded beyond national borders, the need for international cooperation in regulating maritime affairs became evident. In the 19th century, a series of international conventions were adopted, such as the Geneva Convention for the Unification of Certain Rules of Law Respecting Collisions at Sea, which laid the foundation for a global framework of maritime law.
Jurisdiction and Territorial Waters
National Jurisdiction
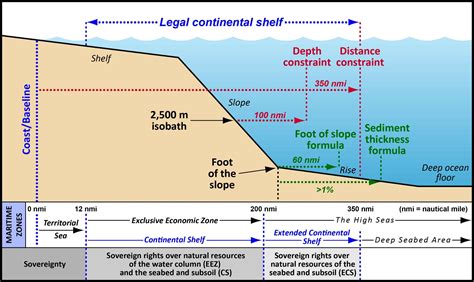
Every nation has the right to establish its own territorial waters, extending outward from its coastline into the sea. Within these territorial waters, the nation has exclusive jurisdiction over all matters, including the regulation of maritime activities. The extent of territorial waters varies from country to country, typically ranging from 3 to 12 nautical miles.
Maritime Boundaries
The boundaries between territorial waters and the high seas are defined by international law. The high seas are considered to be international waters, where no single nation has exclusive jurisdiction. However, certain areas of the high seas may be subject to special regulations, such as those governing fishing or offshore oil exploration.
The Law of the Sea and International Conventions
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is a landmark treaty that codifies the international law of the water maritime. UNCLOS was adopted in 1982 and has been ratified by over 160 nations. It establishes a comprehensive framework for the regulation of all aspects of maritime affairs, including territorial waters, navigation, environmental protection, and dispute resolution.
Other Important International Conventions
In addition to UNCLOS, there are numerous other international conventions that govern specific aspects of maritime law. These include conventions on marine pollution, safety at sea, and the settlement of maritime disputes. These conventions help to ensure the safe and orderly use of the world’s oceans and waterways.
Maritime Contracts and Disputes
Types of Maritime Contracts
Maritime contracts are agreements between parties engaged in maritime activities. These contracts may cover a wide range of matters, including the sale or charter of vessels, the carriage of goods, and marine insurance.
Maritime Disputes
Disputes arising from maritime contracts or other maritime matters are typically resolved through arbitration or litigation. Arbitration is a private, often confidential process in which the parties present their case to a neutral third party, known as an arbitrator. Litigation, on the other hand, involves the resolution of disputes through the court system.
The Future of Maritime Law
Emerging Challenges
The law of the water maritime is constantly evolving to address new challenges and technological advancements. Issues such as climate change, piracy, and the protection of marine biodiversity are gaining increasing attention in the international arena.
Sustainable Maritime Development
Sustainable maritime development is a key priority for the future of maritime law. It involves striking a balance between the economic benefits of maritime activities and the preservation of the marine environment.
Table: Key Concepts in the Law of the Water Maritime
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Territorial waters | The portion of the sea adjacent to the coast over which a nation has exclusive jurisdiction |
| High seas | The portion of the sea beyond territorial waters that is not subject to any nation’s exclusive jurisdiction |
| United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) | A comprehensive treaty that codifies the international law of the water maritime |
| Maritime contract | An agreement between parties engaged in maritime activities |
| Maritime dispute | A conflict arising from a maritime contract or other maritime matter |
| Sustainable maritime development | The concept of balancing economic benefits from maritime activities with the preservation of the marine environment |
Conclusion
Readers, our journey into the fascinating realm of the law of the water maritime has come to an end. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of this complex and ever-evolving field. From the origins of maritime law in ancient times to the latest developments in international regulations, the law of the water maritime continues to shape the way we navigate the world’s oceans and waterways.
As we bid you farewell, we invite you to explore other articles on our website that delve deeper into specific aspects of maritime law. Whether you’re interested in the latest developments in maritime environmental protection, the intricacies of maritime insurance, or the challenges facing the industry in the age of globalization, we have something for everyone. Thank you for joining us on this maritime adventure. May your sails always be filled with the winds of knowledge and understanding.
FAQ About Law of the Water Maritime
What is the Law of the Water Maritime?
Answer: The Law of the Water Maritime is a body of law that governs legal issues related to the sea, including shipping, navigation, and fishing.
What are the main principles of the Law of the Water Maritime?
Answer: The main principles include freedom of the seas, the right of innocent passage, and the obligation to prevent pollution.
What is the history of the Law of the Water Maritime?
Answer: It has a long history dating back to ancient times, with major developments occurring during the Middle Ages and the Age of Exploration.
What are the different types of maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law can be divided into several categories, including admiralty law, shipping law, and marine insurance law.
What are the key legal issues in maritime law?
Answer: Key legal issues include ship collisions, maritime contracts, and environmental protection.
What are the main sources of maritime law?
Answer: The main sources are international treaties, national laws, and customary international law.
How is maritime law enforced?
Answer: Maritime law is enforced through a variety of mechanisms, including national courts, international tribunals, and flag state enforcement.
What are the latest developments in maritime law?
Answer: Recent developments include increasing focus on environmental protection, the rise of autonomous shipping, and the impact of technology on maritime trade.
What are the challenges facing maritime law?
Answer: Challenges include piracy, marine pollution, and the need to balance economic development with environmental protection.
What is the future of maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law is expected to continue to evolve in response to new technologies, global trade, and environmental concerns.




