- Introduction
- The Origins of Maritime Law
- Key Principles of Maritime Law
- Enforcement of Maritime Law
- Maritime Law in the Modern Era
- Table: Key Maritime Laws and Conventions
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about Brief History of Maritime Law
- 1. What is the origin of maritime law?
- 2. How did the Roman Empire influence maritime law?
- 3. What was the role of the Middle Ages in the development of maritime law?
- 4. How did the Renaissance impact maritime law?
- 5. What was the importance of the 17th century in maritime law?
- 6. What was the significance of the 19th century for maritime law?
- 7. How has technology influenced maritime law?
- 8. What is the role of international organizations in maritime law?
- 9. What are some key principles of maritime law?
- 10. How is maritime law enforced?
Introduction
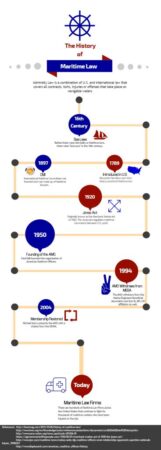
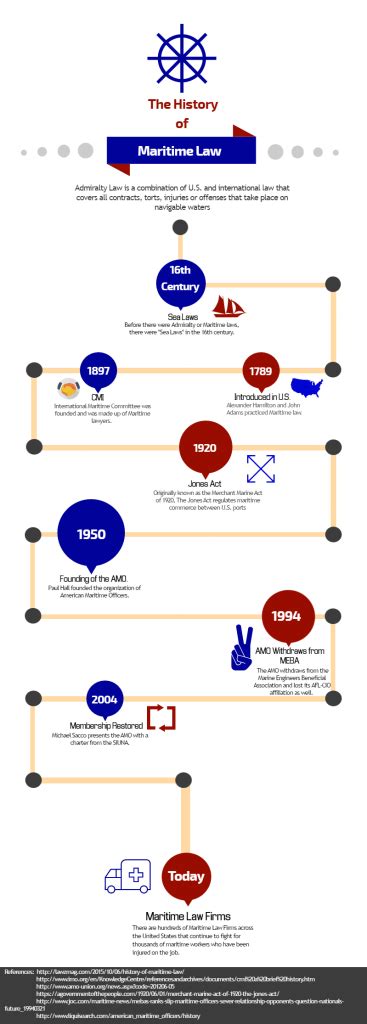
Ahoy, readers! Welcome to our exploration of the rich and captivating world of maritime law. As you set sail on this journey, you’ll discover the fascinating origins, key principles, and enduring legacy that govern the vast and enigmatic realm of the seas.
Maritime law, or admiralty law as it’s sometimes known, has a long and storied history, spanning centuries and continents. From the ancient Mediterranean Sea to the modern-day oceans, this body of law has played a crucial role in regulating maritime commerce, safeguarding seafarers, and protecting marine resources. Join us as we delve into the annals of maritime law, uncovering its origins, unraveling its complexities, and appreciating its enduring importance in the world today.
The Origins of Maritime Law
The roots of maritime law can be traced back to the bustling ports of ancient Greece and Rome. As sea trade flourished, the need for a set of laws governing maritime activities became increasingly apparent. The Rhodian Sea Law, believed to have originated around 1000 B.C., is considered the earliest known maritime code. This code established principles related to ship ownership, cargo liability, and the rights and duties of seafarers.
Over time, maritime law evolved and adapted to the changing needs of the maritime industry. The Middle Ages witnessed the emergence of maritime codes in various European countries, including the Consolato del Mare in Italy and the Laws of Oleron in France. These codes incorporated Roman law principles with local customs and practices, creating a more comprehensive framework for maritime law.
Key Principles of Maritime Law
Maritime law encompasses a wide range of principles and concepts designed to ensure the orderly and equitable functioning of maritime activities. Some of the key principles include:
-
Freedom of the Seas: The high seas are generally considered to be international waters, open to all nations for navigation, fishing, and other lawful purposes.
-
Sovereignty of Coastal States: Coastal states have the right to establish territorial waters and exercise jurisdiction over maritime activities within those waters.
-
Flag State Jurisdiction: Ships are subject to the laws of the flag state under which they are registered. This principle ensures that ships are adequately regulated and inspected to maintain safety standards.
-
Admiralty Jurisdiction: Maritime law cases are typically heard in admiralty courts, which have specialized expertise in maritime matters.
Enforcement of Maritime Law
Enforcing maritime law can be challenging due to the vastness and complexity of the oceans. International cooperation is essential to ensure that laws are upheld and violators are held accountable.
-
International Conventions: Numerous international conventions have been adopted to establish uniform standards for maritime safety, environmental protection, and the prevention of marine pollution.
-
Coast Guard and Naval Forces: Coast guards and naval forces play a vital role in enforcing maritime law within their respective jurisdictions. They conduct patrols, investigate incidents, and apprehend violators.
-
Flag State Responsibility: Flag states have the primary responsibility for enforcing maritime law on ships registered under their flag. This includes conducting inspections, investigating accidents, and prosecuting offenses.
Maritime Law in the Modern Era
Maritime law continues to evolve to meet the challenges of the modern era. Important developments in recent decades have focused on:
-
Environmental Protection: Maritime law has been strengthened to protect marine ecosystems from pollution and overexploitation.
-
Safety and Security: New regulations have been implemented to enhance ship safety and security, including measures to prevent piracy and terrorism.
-
Maritime Arbitration: Arbitration has become an increasingly popular method for resolving maritime disputes due to its efficiency and flexibility.
Table: Key Maritime Laws and Conventions
| Law/Convention | Purpose |
|---|---|
| United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) | Establishes a comprehensive framework for the use of oceans and their resources |
| International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) | Promotes maritime safety, including ship design, construction, and equipment standards |
| International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code) | Regulates the transportation of dangerous goods by sea |
| Maritime Labour Convention, 2006 | Sets minimum standards for seafarers’ working conditions |
| Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter, 1972 (London Dumping Convention) | Prohibits the dumping of hazardous substances into the ocean |
Conclusion
Readers, our voyage into the brief history of maritime law has come to an end. We hope you enjoyed this exploration of the origins, principles, and enforcement mechanisms of this fascinating and complex legal field.
The world’s oceans are vast and unforgiving, but maritime law provides a framework to ensure that maritime activities are conducted in a safe, equitable, and environmentally sustainable manner. As the maritime industry continues to evolve, so too will the laws that govern it. We invite you to explore our other articles on marine law, environmental protection, and international law to further broaden your understanding of these important topics.
FAQ about Brief History of Maritime Law
1. What is the origin of maritime law?
Maritime law has its roots in ancient maritime practices and codes, dating back to the Phoenicians and Greeks.
2. How did the Roman Empire influence maritime law?
The Romans developed a comprehensive legal system that included laws governing maritime matters, known as the Lex Rhodia de Jactu.
3. What was the role of the Middle Ages in the development of maritime law?
The rise of maritime trade in the Middle Ages led to the emergence of maritime courts and the adoption of customary laws and ordinances.
4. How did the Renaissance impact maritime law?
The Renaissance witnessed an increased focus on maritime trade and exploration, resulting in the development of new laws and treaties.
5. What was the importance of the 17th century in maritime law?
The 17th century saw the rise of nation-states and the establishment of admiralty courts, which adjudicated maritime disputes.
6. What was the significance of the 19th century for maritime law?
The 19th century marked the globalization of maritime trade and the development of international maritime conventions.
7. How has technology influenced maritime law?
Technological advancements in shipping and communication have led to new legal issues and regulations in maritime law.
8. What is the role of international organizations in maritime law?
International organizations such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) play a crucial role in developing and enforcing maritime regulations.
9. What are some key principles of maritime law?
Key principles include jurisdiction over maritime disputes, the doctrine of general average, and the law of salvage.
10. How is maritime law enforced?
Maritime law is enforced through a combination of national courts, international tribunals, and administrative agencies.