
- Introduction
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- Regional Maritime Environmental Protection
- Table: Summary of Key International Conventions on Maritime Environmental Protection
- Challenges and Future Trends
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about Environmental Laws at a Global Level for Maritime
- What is the purpose of environmental laws in maritime?
- What are the key international agreements on maritime environmental protection?
- What is the MARPOL Convention?
- What does the London Convention regulate?
- How does the Barcelona Convention protect the Mediterranean Sea?
- What is the purpose of the International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments?
- What is the role of the International Maritime Organization (IMO)?
- How are maritime environmental laws enforced?
- What are the challenges to enforcing maritime environmental laws?
- What can individuals do to support maritime environmental protection?
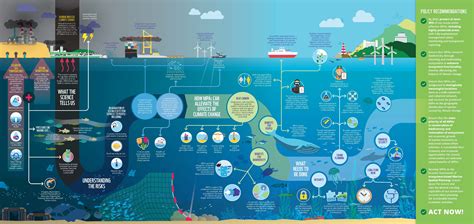
Introduction
Hey readers! Welcome to our comprehensive guide on environmental laws at a global level, specifically focusing on maritime regulations. In today’s interconnected world, protecting our oceans and waterways is more critical than ever. This article will delve into the various international agreements, conventions, and organizations that govern maritime environmental protection, ensuring the health and sustainability of our precious oceans.
Environmental laws at a global level for maritime activities aim to minimize pollution, preserve marine biodiversity, and manage resources responsibly. These laws have evolved over time to address emerging challenges and reflect scientific advancements. Whether you’re a concerned citizen, a maritime industry professional, or simply curious about the legal framework surrounding our oceans, this article will provide you with valuable insights.
International Maritime Organization (IMO)
The Guardian of Global Maritime Safety and Environment
Established in 1948, the IMO is the leading international body responsible for developing and enforcing environmental laws for maritime activities. It has over 170 member states and serves as a forum for cooperation and coordination among governments, the shipping industry, and other stakeholders. The IMO’s mandate includes:
- Preventing pollution from ships
- Enhancing maritime safety
- Facilitating cooperation on technical matters
- Promoting sustainable shipping practices
Key IMO Conventions
The IMO has adopted several landmark conventions that set global standards for maritime environmental protection. These include:
- The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL)
- The International Convention on the Control of Harmful Anti-fouling Systems on Ships (AFS)
- The International Convention on Salvage (1989)
- The International Convention on Oil Pollution Preparedness, Response and Cooperation (OPRC)
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
The Comprehensive Framework for Ocean Governance
UNCLOS is a comprehensive multilateral treaty that provides the legal framework for all activities in the world’s oceans and seas. Adopted in 1982, UNCLOS establishes the rights and responsibilities of states regarding maritime boundaries, navigation, environmental protection, and resource management.
UNCLOS and Maritime Environment
UNCLOS includes provisions specifically aimed at protecting the marine environment. For example, it requires states to:
- Take measures to prevent, reduce, and control pollution from ships and other sources
- Cooperate in combating marine pollution emergencies
- Conserve marine living resources and protect endangered species
- Conduct scientific research and share environmental data
Regional Maritime Environmental Protection
In addition to global agreements, regional organizations also play a significant role in maritime environmental protection. These organizations coordinate efforts among member states and develop regional regulations to address specific challenges. Some notable examples include:
- The European Union (EU): The EU has adopted a comprehensive framework of environmental laws, including the Marine Strategy Framework Directive, which aims to achieve good environmental status in all European seas by 2020.
- The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD): The OECD promotes sustainable maritime practices and provides guidance to member states on environmental policy and regulation.
- The Arctic Council: The Arctic Council is a forum for cooperation among Arctic states on environmental protection, including measures to address the impacts of climate change and shipping activities.
Table: Summary of Key International Conventions on Maritime Environmental Protection
| Convention | Purpose | Main Provisions |
|---|---|---|
| MARPOL | Preventing pollution from ships | Regulations on discharge of oil, chemicals, garbage, and sewage |
| AFS | Controlling harmful anti-fouling systems | Ban on the use of certain toxic anti-fouling paints |
| Salvage | Regulating salvage operations | Establishes procedures and principles for salvage operations at sea |
| OPRC | Enhancing oil pollution preparedness and response | Requires states to develop national oil spill response plans and cooperate in combating spills |
| UNCLOS | Providing a comprehensive framework for ocean governance | Establishes rights and responsibilities of states regarding maritime boundaries, environmental protection, and resource management |
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite progress in developing and implementing environmental laws at a global level, many challenges remain in protecting the marine environment. These include:
- Enforcing regulations and ensuring compliance
- Addressing emerging threats, such as plastic pollution and climate change
- Promoting sustainable shipping practices
- Balancing economic development with environmental protection
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the future of maritime environmental law. These include:
- Increased focus on climate change mitigation and adaptation
- Advancements in technology and innovation for environmental monitoring and enforcement
- Enhanced cooperation and collaboration among stakeholders
- Continued efforts to strengthen and harmonize global and regional regulations
Conclusion
Environmental laws at a global level play a vital role in protecting the health of our oceans and waterways. Through international agreements, conventions, and organizations, governments and stakeholders collaborate to address maritime environmental challenges and ensure sustainable shipping practices. While progress has been made, ongoing efforts are necessary to strengthen enforcement, promote innovation, and balance economic development with environmental protection.
Readers, if you found this article informative, we encourage you to explore our other articles on maritime law, environmental policy, and sustainability. Stay updated on the latest developments and join the global movement to protect our oceans for generations to come.
FAQ about Environmental Laws at a Global Level for Maritime
What is the purpose of environmental laws in maritime?
To protect the marine environment from pollution and degradation caused by human activities, such as shipping, fishing, and offshore oil exploration.
What are the key international agreements on maritime environmental protection?
The MARPOL Convention, London Convention, Barcelona Convention, and International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments.
What is the MARPOL Convention?
The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, designed to prevent and minimize pollution of the marine environment by ships.
What does the London Convention regulate?
The dumping of waste at sea, requiring parties to take all practical steps to prevent pollution of the marine environment.
How does the Barcelona Convention protect the Mediterranean Sea?
By addressing pollution, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable development through cooperation among Mediterranean countries.
What is the purpose of the International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments?
To prevent the introduction of harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens into new environments through ballast water exchange.
What is the role of the International Maritime Organization (IMO)?
To develop and adopt global regulations for the safety and environmental performance of international shipping.
How are maritime environmental laws enforced?
Through inspections, audits, and sanctions by national authorities and international organizations like the IMO.
What are the challenges to enforcing maritime environmental laws?
Lack of resources, weak enforcement mechanisms, and limited international cooperation.
What can individuals do to support maritime environmental protection?
Reduce their carbon footprint, choose sustainable seafood, and support organizations working to protect the marine environment.



