
- Introduction
- Understanding Forex Hedging
- Types of Forex Hedging Strategies
- Benefits of Hedging with Forex.com
- Forex Hedging Table Breakdown
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about Forex.com Hedge
- What is a hedge in Forex?
- Why do traders use hedges?
- What are the different types of hedges?
- What are the benefits of hedging?
- What are the risks of hedging?
- How do I create a hedge?
- What is the best way to manage a hedge?
- When should I use a hedge?
- How much should I hedge?
- Are there any alternatives to hedging?
Introduction
Greetings, readers! Today, we embark on a journey into the realm of forex hedging, a powerful tool for mitigating risk in the ever-fluctuating forex market. With Forex.com, a renowned forex broker, hedging becomes a breeze, empowering you to navigate market volatility with confidence.
As we delve into this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover the intricacies of Forex.com hedging, explore its various strategies, and grasp the benefits it offers. Join us as we unlock the secrets to risk management and enhance your forex trading experience.
Understanding Forex Hedging
What is Forex Hedging?
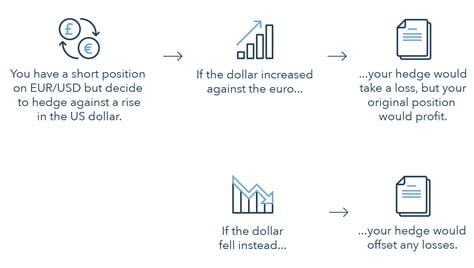
Forex hedging entails entering into an opposing position in the same currency pair to offset potential losses arising from price fluctuations in the primary position. For instance, if you long EUR/USD, you could hedge by simultaneously shorting EUR/USD or buying USD/EUR.
Why Use Forex Hedging?
Hedging provides a safety net against market risks. By offsetting positions, you reduce the overall risk exposure and maintain your trading capital’s integrity. It also allows you to lock in profits, preventing potential losses from eroding your earnings.
Types of Forex Hedging Strategies
Pair Hedging
Pair hedging involves offsetting positions in the same currency pair. This strategy mitigates risk when you expect price movements to be relatively stable within a specific range. Forex.com’s advanced trading platform makes pair hedging seamless.
Cross Hedging
Cross hedging entails using a different currency pair to hedge the primary position. This strategy is suitable when you anticipate price movements to be correlated between different currency pairs. Forex.com’s diverse currency offerings empower you to explore various cross-hedging options.
Spread Hedging
Spread hedging involves buying and selling the same currency pair at different strike prices. This strategy helps limit losses in a range-bound market. Forex.com’s flexible order types enable you to implement spread hedging with precision.
Benefits of Hedging with Forex.com
Risk Mitigation
Forex.com’s robust hedging tools empower you to minimize risk exposure and protect your trading capital. Their advanced trading platform allows for quick and efficient hedging executions.
Profit Protection
Hedging allows you to lock in profits, ensuring you retain your earnings even in volatile market conditions. Forex.com’s flexible hedging strategies enable you to secure your profits and avoid potential setbacks.
Flexible Hedging Options
Forex.com offers a wide range of hedging options, catering to diverse trading styles and risk tolerances. Whether you prefer pair hedging, cross hedging, or spread hedging, Forex.com has you covered.
Forex Hedging Table Breakdown
| Hedging Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pair Hedging | Offset positions in the same currency pair | Minimal risk exposure, suitable for stable markets |
| Cross Hedging | Hedge with a different currency pair | Correlated price movements, suitable for cross-market hedging |
| Spread Hedging | Buy and sell at different strike prices | Limited losses in range-bound markets |
Conclusion
Exploring the world of forex com hedge with Forex.com empowers you to manage risk and enhance your trading performance. Their advanced hedging tools, diverse strategies, and seamless execution capabilities make Forex.com the ideal partner for risk-conscious traders.
As you continue your forex journey, remember to explore our other articles on forex trading, risk management, and market analysis. Knowledge is power, and with Forex.com as your trusted broker, you can navigate the forex landscape with confidence and reap the rewards that await you.
FAQ about Forex.com Hedge
What is a hedge in Forex?
A hedge in Forex is a position that is taken to offset the risk of another position. This can be done by taking a position in the opposite direction of the original position, or by taking a position in a correlated asset.
Why do traders use hedges?
Traders use hedges to reduce the risk of their positions. By taking a hedge, a trader can limit the potential losses that they could incur on their original position.
What are the different types of hedges?
There are two main types of hedges: natural hedges and synthetic hedges. Natural hedges involve taking a position in the opposite direction of the original position, while synthetic hedges involve taking a position in a correlated asset.
What are the benefits of hedging?
The benefits of hedging include reducing the risk of losses, improving the Sharpe ratio of a portfolio, and freeing up capital for other investments.
What are the risks of hedging?
The risks of hedging include the possibility of losing money on the hedge position, and the possibility that the hedge will not be effective in reducing the risk of the original position.
How do I create a hedge?
There are a number of different ways to create a hedge. The most common method is to take a position in the opposite direction of the original position. Another method is to take a position in a correlated asset.
What is the best way to manage a hedge?
The best way to manage a hedge is to monitor the performance of both the original position and the hedge position. If the hedge is not effective in reducing the risk of the original position, it may need to be adjusted or removed.
When should I use a hedge?
A hedge should be used when the risk of a position is too high. This can be the case when the position is large, when the market is volatile, or when the trader is not confident in the direction of the market.
How much should I hedge?
The amount of hedging that is appropriate will vary depending on the individual trader and the specific situation. However, a good rule of thumb is to hedge no more than 50% of the original position.
Are there any alternatives to hedging?
There are a number of alternatives to hedging, such as stop-loss orders, limit orders, and trailing stops. However, hedges are often the most effective way to reduce the risk of a position.



