- Forwards Forex: A Comprehensive Guide
- Types of Forwards Forex
- Advantages of Forwards Forex
- Considerations for Forwards Forex
- Forwards Forex Market
- Forward Forex Example
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about Forwards Forex
- What is forward forex?
- When is a forward contract used?
- How is the forward rate determined?
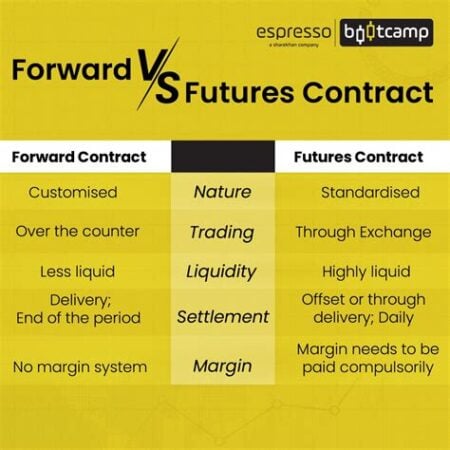
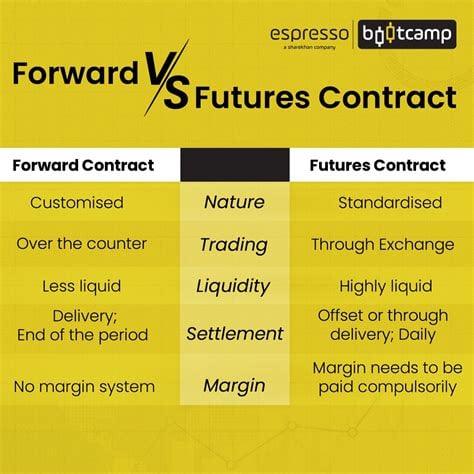
- What is the difference between a forward and a futures contract?
- How is a forward contract settled?
- What are the advantages of using forwards?
- What are the disadvantages of using forwards?
- How is a forward contract priced?
- What are the risks associated with forward forex?
- How is a forward contract terminated?
Forwards Forex: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Salutations, readers! Welcome to the realm of forwards forex, where finance, risk management, and opportunity intersect. Let’s embark on an educational journey, exploring the nuances and practicalities of this fascinating financial instrument.
Forex forwards, also known as forward currency contracts, are agreements to buy or sell a predetermined amount of a currency at a specified future date and price. Unlike spot forex transactions, which settle immediately, forwards provide a structured framework for managing foreign exchange (FX) risk over a longer time horizon.
Types of Forwards Forex
1. Direct or Standard Forwards
These are the most common type of forwards, where two parties directly exchange currencies at a future date.
2. Non-Deliverable Forwards (NDFs)
NDFs are settled in cash rather than physically exchanging currency. They are often used in markets with currency restrictions or high exchange rate volatility.
Advantages of Forwards Forex
1. Risk Management
Forwards allow businesses and individuals to lock in future exchange rates, reducing the risk of unfavorable currency fluctuations.
2. Arbitrage Opportunities
Forwards can be used to exploit price discrepancies between spot and future markets, creating profit-making opportunities.
3. Hedging Strategies
Forwards can be incorporated into hedging strategies to neutralize the impact of FX risk on underlying financial positions.
Considerations for Forwards Forex
1. Counterparty Risk
Forwards involve counterparty risk, as both parties must fulfill their obligations. Choosing reputable counterparties is crucial.
2. Cost of Carry
The cost of carry, which includes interest rate differentials and holding costs, affects the overall profitability of forwards contracts.
3. Volatility Risk
Forwards can be subject to price fluctuations, particularly in volatile market conditions. Careful monitoring and risk assessment are essential.
Forwards Forex Market
1. Trading Instruments
Forwards are traded in the over-the-counter (OTC) market, where individual contracts can be tailored to specific needs.
2. Market Participants
Banks, financial institutions, businesses, and investors are the primary participants in the forwards forex market.
3. Factors Influencing Forward Prices
Forward prices are determined by spot prices, interest rate differentials, market expectations, and political and economic factors.
Forward Forex Example
Consider a company importing goods from Japan. They enter into a 90-day forward contract to buy 10 million Japanese Yen (JPY) at a rate of 1 USD = 110 JPY. This ensures that they will receive the JPY they need at a fixed rate, regardless of exchange rate fluctuations in the future.
Conclusion
Forwards forex are versatile financial instruments that offer risk management, hedging, and arbitrage opportunities in the foreign exchange market. By understanding the types, advantages, and considerations associated with forwards, you can harness their potential to enhance your financial strategy.
If you’re eager to learn more about forwards forex or explore other financial topics, be sure to check out our other articles. We’ve covered a wide range of subjects, from portfolio optimization to blockchain applications. Join us on this educational journey and equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the financial world.
FAQ about Forwards Forex
What is forward forex?
An agreement to buy or sell a currency at a specific exchange rate on a future date.
When is a forward contract used?
To hedge against potential currency fluctuations or to speculate on currency movements.
How is the forward rate determined?
Based on the spot exchange rate, interest rate differentials, and market expectations.
What is the difference between a forward and a futures contract?
Forwards are tailored to specific parties and are not standardized, while futures are standardized contracts traded on exchanges.
How is a forward contract settled?
By delivering the agreed-upon amount of currency on the specified date and receiving the agreed-upon price.
What are the advantages of using forwards?
Hedging, price locking, and speculating on currency movements.
What are the disadvantages of using forwards?
Lack of liquidity, potential for loss due to adverse currency fluctuations, and the need for a counterparty.
How is a forward contract priced?
The forward rate is the spot rate plus or minus the carry, which is the cost of carry or the benefit of carry.
What are the risks associated with forward forex?
Currency fluctuations, counterparty risk, and market risk.
How is a forward contract terminated?
By offsetting it with a reverse contract or by failing to deliver on the contract date.