- High Stakes on the High Seas: Navigating the Complexities of Maritime Law
-
FAQs about High Stakes on the High Seas Maritime Law
- What is maritime law?
- What are some of the key elements of maritime law?
- What are some of the most common types of maritime law cases?
- Who enforces maritime law?
- What are the penalties for violating maritime law?
- What are some of the challenges in enforcing maritime law?
- What are some of the current trends in maritime law?
- How can I learn more about maritime law?
- What makes a maritime law case high-stakes?
- What are some examples of high-stakes maritime law cases?
High Stakes on the High Seas: Navigating the Complexities of Maritime Law
Introduction
Greetings, readers! Welcome to the vast and captivating realm of maritime law, where the stakes are high and the high seas hold countless legal complexities. From the depths of international waters to the shores of every continent, maritime law governs the interactions, disputes, and regulations that shape the world’s oceans. Join us as we embark on a comprehensive exploration of this intriguing field, delving into its nuances and highlighting the potential perils and rewards it holds.
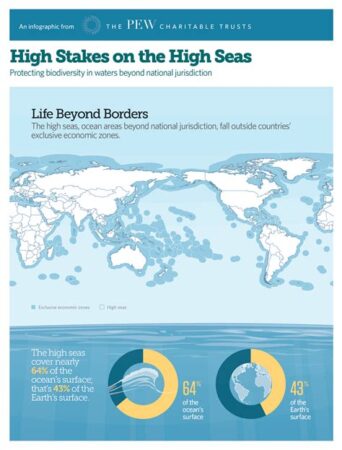
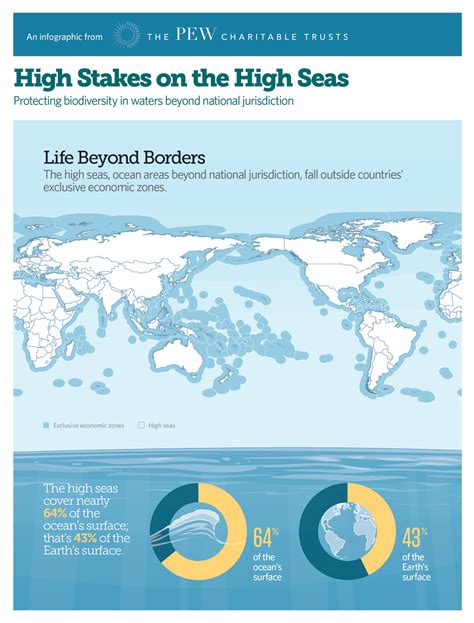
The high stakes involved in maritime law stem from the intrinsic value and inherent risks associated with the maritime industry. The transportation of goods, the exploration of resources, and the pursuit of adventure all take place within the vast expanse of our oceans. As a result, disputes over territory, resources, environmental protection, and safety concerns frequently arise, demanding a comprehensive and sophisticated legal framework to resolve them.
Disputes Over Territorial Waters
Territorial waters, extending typically 12 nautical miles from a nation’s coastline, serve as a crucial point of contention in maritime law. These waters fall under the exclusive jurisdiction of the coastal state, granting it the authority to regulate activities such as fishing, navigation, and resource extraction. Disputes over territorial waters often arise when nations disagree on maritime boundaries, leading to tensions and even military conflicts.
Environmental Regulations
The high seas, once considered a vast, untamed wilderness, are now facing unprecedented environmental challenges. Maritime activities such as shipping, fishing, and offshore drilling can have detrimental effects on marine ecosystems, threatening biodiversity and contributing to pollution. In response, international agreements and national regulations have been established to protect the marine environment, ensuring the sustainable use of resources and the preservation of our oceans for generations to come.
Piracy and Security Threats
The high seas are not immune to the perils of lawlessness and security threats. Piracy, a scourge on the seas for centuries, continues to plague certain regions, threatening the safety of seafarers and disrupting global trade. Armed robbery, kidnapping, and extortion are common tactics employed by modern-day pirates, prompting international cooperation and efforts to combat this menace.
Table: Key Concepts in Maritime Law
| Aspect | Key Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Territorial Waters | Exclusive Economic Zone | A maritime zone extending 200 nautical miles from a nation’s coastline, granting it limited sovereign rights to explore and exploit resources. |
| Marine Environmental Protection | MARPOL | The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, regulating the discharge of harmful substances into the marine environment. |
| Anti-Piracy Measures | United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea | An international treaty that outlines the legal framework for combating piracy and promoting cooperation among nations. |
| Safety at Sea | International Maritime Organization | A specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting maritime safety, preventing pollution, and ensuring the welfare of seafarers. |
| Maritime Insurance | P&I Clubs | Protection and Indemnity clubs that provide insurance coverage for maritime activities, such as liability for accidents, injury, and environmental damage. |
Enforcement and Compliance
Enforcing maritime laws presents a unique set of challenges. The vastness of the oceans and the mobility of vessels make it difficult to monitor and apprehend violators. International cooperation is essential in combating illegal activities and ensuring compliance with regulations. Collaborative efforts between navies, coast guards, and regulatory agencies are crucial for upholding the rule of law on the high seas.
Technology and Innovation
Technology is playing an increasingly significant role in maritime law. Advanced satellite and tracking systems enhance surveillance capabilities, enabling authorities to detect and respond to violations in real-time. Electronic navigation charts and communication systems improve safety and efficiency at sea. As technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly reshape the landscape of maritime law enforcement and regulation.
Conclusion
The complexities of the high seas demand a robust and enduring legal framework capable of addressing the challenges and opportunities it presents. Maritime law serves as the guiding compass, ensuring the safe, sustainable, and equitable use of our oceans. By understanding the intricate web of regulations, disputes, and security threats that shape maritime law, we can appreciate the vital role it plays in safeguarding the future of our oceans and the well-being of those who sail upon them.
Don’t forget to explore our other articles on related topics:
- The Allure and Enigmas of International Maritime Law
- Environmental Stewardship on the High Seas: A Legal Perspective
- Combating Piracy: Uniting Nations Against the Scourge of the Seas
FAQs about High Stakes on the High Seas Maritime Law
What is maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law, also known as admiralty law, governs legal issues related to ships, seafaring, and navigation.
What are some of the key elements of maritime law?
Answer: Key elements include:
- Admiralty law: Deals with cases involving ships, admiralty and maritime claims, and maritime contracts.
- Law of the sea: Regulates the rights and responsibilities of nations in relation to their use of the oceans.
- International maritime law: Governs maritime commerce, including ship registration, navigation, and safety.
What are some of the most common types of maritime law cases?
Answer: Common cases include:
- Shipping accidents
- Personal injuries
- Cargo disputes
- Admiralty seizures
- Maritime divorces
Who enforces maritime law?
Answer: Maritime law is enforced by various entities, including:
- Coast Guard
- Law enforcement agencies
- Maritime courts
- International tribunals
What are the penalties for violating maritime law?
Answer: Penalties can range from fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation.
What are some of the challenges in enforcing maritime law?
Answer: Challenges include:
- Vastness of the oceans
- Jurisdiction issues
- Complexities of maritime trade and regulations
What are some of the current trends in maritime law?
Answer: Trends include:
- Increased focus on environmental protection
- Automation and technology advancements
- Globalization of maritime transportation
How can I learn more about maritime law?
Answer: You can learn more through:
- Law school programs
- Continuing education courses
- Textbooks and legal resources
- Industry conferences and webinars
What makes a maritime law case high-stakes?
Answer: High-stakes cases may involve:
- Loss of life or significant injuries
- Substantial financial losses
- Complex legal and jurisdictional issues
- Reputational damage
What are some examples of high-stakes maritime law cases?
Answer: Examples include:
- The BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill
- The Costa Concordia cruise ship disaster
- The MV Sea-Land Express container ship fire