
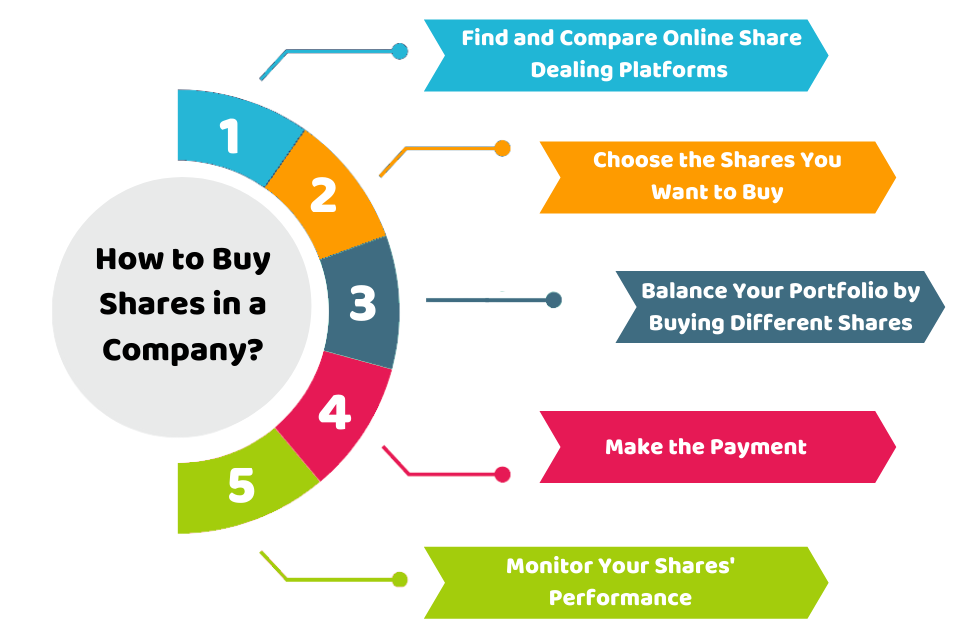
How do you buy stock? It’s a question that’s probably crossed your mind, especially if you’ve heard about the potential for impressive returns. But with all the jargon and different platforms, it can seem intimidating. Don’t worry, though! Investing in the stock market isn’t as complicated as it seems. In this guide, we’ll break down the steps, starting with the basics and leading you through the process of researching, buying, and managing your stock investments.
Think of it like this: buying stock is like owning a tiny piece of a company. When the company does well, the value of your stock goes up, and you could make money. But just like any investment, there’s also a risk that the value could go down. We’ll talk about how to manage that risk and make smart decisions.
Understanding the Basics
Stocks are a fundamental part of the financial world, representing ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder, owning a small piece of the company. This ownership entitles you to a share of the company’s profits, called dividends, and the right to vote on important company decisions.
Types of Stocks
There are two main types of stocks: common stock and preferred stock. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
- Common Stock: The most common type of stock, representing basic ownership in a company. Common stockholders have voting rights and receive dividends based on the company’s performance. They also have the potential for higher returns but also face greater risk.
- Preferred Stock: A type of stock that offers investors priority over common stockholders in terms of dividends and asset distribution during liquidation. Preferred stockholders typically have a fixed dividend rate and may not have voting rights. This type of stock is generally considered less risky than common stock.
Stock Markets
Stock markets serve as platforms for buying and selling stocks. These markets are essential for facilitating stock trading, allowing investors to buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. They provide a central location where buyers and sellers can meet and negotiate prices, creating a transparent and efficient system for trading stocks.
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): One of the largest and most well-known stock exchanges in the world. The NYSE is known for its high trading volume and stringent listing requirements.
- Nasdaq: Another major stock exchange, known for its focus on technology and growth companies. Nasdaq is an electronic exchange, meaning that trades are conducted online.
Stock markets play a vital role in the economy, providing capital for companies to grow and creating opportunities for investors to participate in the growth of businesses.
Opening a Brokerage Account
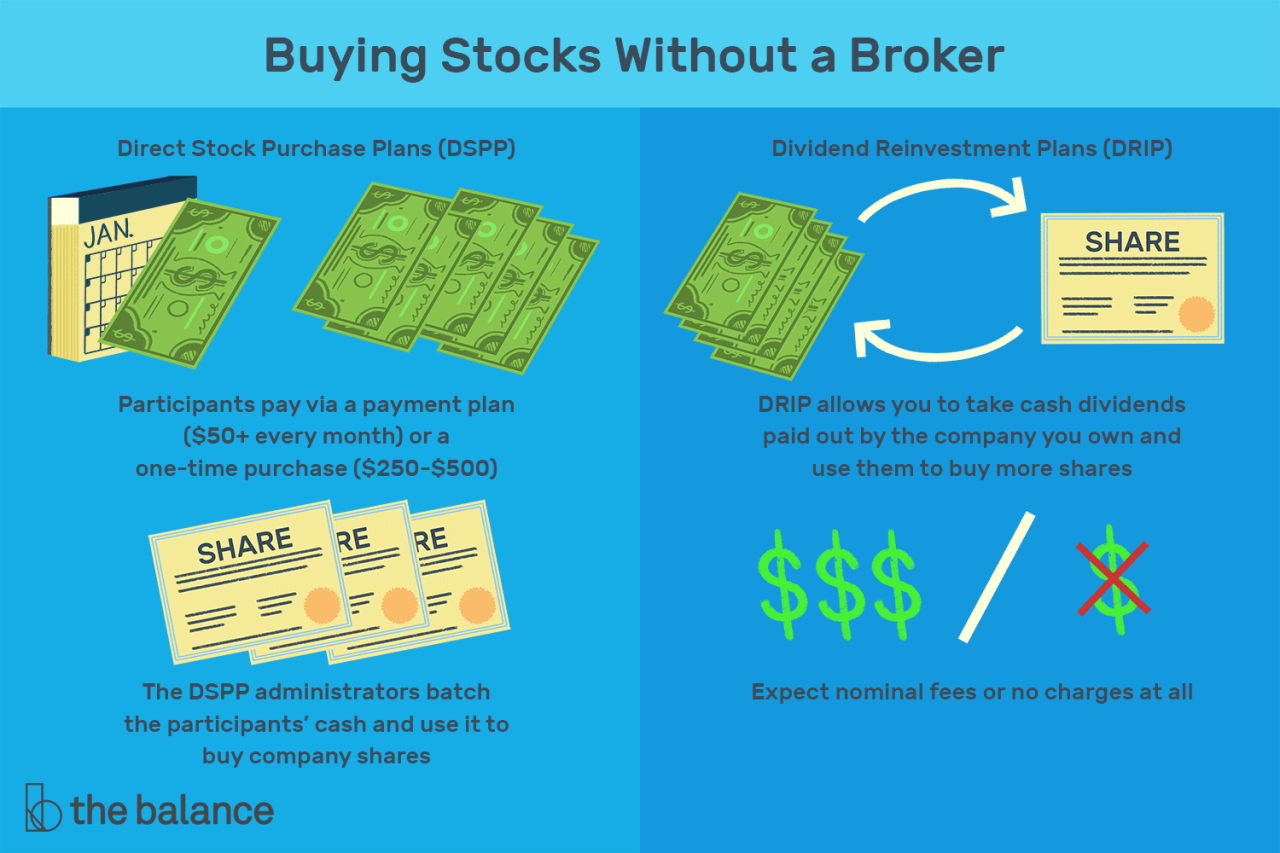
Before you can start investing in the stock market, you need to open a brokerage account. This account will hold your money and allow you to buy and sell stocks. It’s like a bank account, but specifically designed for investing.
Choosing a Brokerage
Choosing the right brokerage is an important first step. Different brokerages offer varying services, fees, and features. Here are some factors to consider:
- Fees: Some brokerages charge commission fees for every trade, while others offer commission-free trading. Some also have monthly fees or minimum balance requirements.
- Research Tools: Some brokerages offer extensive research tools, such as stock analysis, market data, and charting tools, which can be helpful for making investment decisions.
- Investment Options: Different brokerages offer different investment options, such as stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds. Make sure the brokerage offers the investment options you are interested in.
- Customer Support: Consider the brokerage’s customer support options, including phone, email, and live chat. You want to make sure you can easily get help when you need it.
Once you’ve chosen a brokerage, you’ll need to open an account.
Opening a Brokerage Account
The process of opening a brokerage account is generally straightforward. Here are the typical steps involved:
- Visit the Brokerage’s Website: Go to the website of the brokerage you’ve chosen and click on the “Open an Account” or “Sign Up” button.
- Provide Personal Information: You’ll need to provide your personal information, such as your name, address, Social Security number, date of birth, and email address.
- Choose an Account Type: You’ll need to choose the type of account you want to open, such as an individual account, joint account, or trust account.
- Provide Financial Information: You’ll need to provide information about your financial situation, such as your income, assets, and liabilities.
- Answer Security Questions: You’ll need to answer security questions to verify your identity and protect your account.
- Fund Your Account: Once your account is approved, you’ll need to fund it by transferring money from your bank account.
Account Verification and Funding
After you submit your application, the brokerage will verify your identity and financial information. This process typically involves:
- Identity Verification: The brokerage may require you to provide documents, such as a driver’s license or passport, to verify your identity.
- Credit Check: The brokerage may also perform a credit check to assess your financial history.
- Account Funding: Once your account is verified, you can fund it by transferring money from your bank account. Most brokerages offer various funding methods, such as bank transfers, wire transfers, and debit cards.
Required Documentation and Information
To open a brokerage account, you’ll typically need to provide the following information:
- Personal Information: Your full name, address, Social Security number, date of birth, and email address.
- Financial Information: Your income, assets, and liabilities. You may be asked to provide documentation, such as pay stubs or bank statements.
- Investment Experience: Some brokerages may ask about your investment experience, such as your level of knowledge and trading history.
- Tax Information: You may need to provide your tax identification number (TIN) or Social Security number.
Tips for Choosing a Username and Password
Choosing a strong username and password is crucial for protecting your brokerage account from unauthorized access. Here are some tips:
- Avoid Using Personal Information: Don’t use your name, birthday, or other easily guessable information in your username or password.
- Use a Combination of Uppercase and Lowercase Letters, Numbers, and Symbols: This makes your password more difficult to crack.
- Choose a Password You Can Remember: Avoid using passwords that are too complex or difficult to remember. You can use a password manager to store your passwords securely.
- Don’t Use the Same Password for Multiple Accounts: If one account is compromised, your other accounts may be at risk if you use the same password.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: This adds an extra layer of security to your account by requiring you to enter a code from your phone or email in addition to your password.
Monitoring Your Investments: How Do You Buy Stock

Investing in the stock market is a long-term game, and it’s crucial to keep a close eye on your portfolio’s performance. Just like you wouldn’t leave your car running without checking the dashboard, you shouldn’t let your investments run on autopilot. Monitoring your investments allows you to stay informed about your progress, make adjustments when necessary, and ensure you’re on track to meet your financial goals.
Tools and Resources for Monitoring Your Investments
Monitoring your investments doesn’t have to be a daunting task. Several tools and resources can help you track your portfolio’s performance and stay informed about market trends.
- Brokerage Account Statements: Your brokerage account statements provide a detailed breakdown of your investments, including purchase and sale history, dividends received, and current market value. Regularly reviewing your statements helps you understand your portfolio’s performance and identify any areas that need attention.
- Portfolio Tracking Apps: Numerous apps are available for both desktop and mobile devices that can help you track your investments in real-time. These apps often provide features such as performance charts, risk analysis, and personalized recommendations. Popular options include Personal Capital, Betterment, and Robinhood.
- Financial News Websites and Apps: Staying informed about market trends is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Websites and apps like Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, and MarketWatch provide real-time market data, news updates, and expert analysis. These resources can help you understand the factors driving market fluctuations and make adjustments to your portfolio as needed.
Adjusting Your Investment Strategy
Market conditions are constantly changing, and your investment strategy should adapt to these fluctuations. Monitoring your investments allows you to identify opportunities to rebalance your portfolio, adjust your risk tolerance, or even take advantage of market dips to buy more shares at a lower price.
“A good investor is always learning and adapting to changing market conditions.” – Warren Buffett
For example, if the market is experiencing a downturn and your portfolio is losing value, you might consider shifting your investments toward more conservative options, such as bonds or cash. Conversely, if the market is experiencing a bull run and your portfolio is growing steadily, you might consider increasing your exposure to riskier assets like growth stocks.
Remember, adjusting your investment strategy should always be aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. It’s essential to consult with a financial advisor if you have any questions or need help making investment decisions.
Managing Your Investments
Once you’ve dipped your toes into the stock market waters, it’s time to think about the bigger picture—managing your investments for the long haul. This involves more than just buying and holding; it’s about strategically navigating the ups and downs of the market to achieve your financial goals.
Diversification, How do you buy stock
Diversification is the key to reducing risk in investing. Think of it like spreading your eggs across different baskets. By investing in a variety of assets, like stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, you’re less likely to lose everything if one particular investment tanks.
“Don’t put all your eggs in one basket” – A common proverb that perfectly illustrates the concept of diversification.
Investment Strategies
There are several investment strategies you can employ, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are a few popular ones:
- Value Investing: This strategy focuses on finding undervalued stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value. Value investors look for companies with strong fundamentals, like solid earnings, low debt, and a history of profitability. They believe that the market will eventually recognize the true value of these companies and their stock prices will rise.
- Growth Investing: This strategy focuses on companies that are expected to grow rapidly in the future. Growth investors look for companies with innovative products or services, strong management teams, and a large market opportunity. They are willing to pay a premium for these companies, expecting their stock prices to appreciate significantly over time.
- Dividend Investing: This strategy focuses on companies that pay regular dividends to their shareholders. Dividend investors look for companies with a long history of dividend payments, a stable business model, and a strong balance sheet. They can enjoy a steady stream of income from their investments, while also potentially benefiting from stock price appreciation.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
As your investments grow and the market fluctuates, your portfolio’s asset allocation (the mix of different investments) may drift away from your original goals. Rebalancing involves adjusting your portfolio to bring it back in line with your desired allocation.
For example, if you started with a 60/40 stock/bond portfolio and stocks have performed exceptionally well, your portfolio might become 70/30. To rebalance, you could sell some of your stocks and use the proceeds to buy more bonds, bringing the allocation back to 60/40.
Rebalancing helps to:
- Maintain your risk tolerance: As your portfolio shifts, your risk exposure may change. Rebalancing ensures that your risk level stays consistent with your investment goals.
- Capitalize on market opportunities: When one asset class performs well, rebalancing allows you to take advantage of potential growth in other asset classes that may be lagging.
- Reduce potential losses: By selling some of your investments when they are performing well and buying more of those that are lagging, you can help to mitigate potential losses if the market takes a downturn.
Epilogue
So, you’ve got the basics of buying stock, but remember, investing is a marathon, not a sprint. Take your time, do your research, and don’t be afraid to ask questions. The stock market can be a powerful tool for building wealth, but it’s important to approach it with a clear head and a solid plan. And hey, if you’re still feeling a little unsure, there are tons of resources out there to help you along the way. Now go forth and invest wisely!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some popular stock trading apps?
There are many popular stock trading apps out there, including Robinhood, TD Ameritrade, and Fidelity. Each has its own features and fees, so it’s important to compare them before choosing one.
How much money do I need to start investing in stocks?
You don’t need a lot of money to start investing. Many brokerage accounts allow you to buy fractional shares, which means you can buy a portion of a stock even if you don’t have enough to buy a whole share. You can also start with a small amount and invest regularly over time.
Is it safe to invest in the stock market?
Investing in the stock market always carries some risk. However, you can mitigate that risk by diversifying your portfolio, doing your research, and investing for the long term. It’s important to remember that you should never invest money you can’t afford to lose.
What is a dividend?
A dividend is a payment made by a company to its shareholders, typically from its profits. Dividends can be paid in cash or stock, and they can be a source of income for investors.





