
How to invest in stock is a question that many people ask, and it’s a great one! The stock market can be a powerful tool for building wealth over time, but it can also be intimidating for beginners. This guide will walk you through the basics of investing in stocks, from understanding the market to making your first purchase.
We’ll cover everything you need to know to get started, including choosing a brokerage account, researching companies, and developing an investment strategy. We’ll also discuss important concepts like diversification and risk management, and provide tips for managing your portfolio and avoiding common mistakes.
Understanding the Stock Market
Think of the stock market as a giant marketplace where people buy and sell tiny pieces of ownership in companies, called stocks. These pieces are like slices of a pizza, and each slice represents a share of the company’s profits and losses.
Stocks and How They Work
When you buy a stock, you become a part-owner of the company. The price of a stock is determined by supply and demand, meaning the more people want to buy a stock, the higher its price goes. The opposite is also true: if more people want to sell a stock, its price will drop.
The value of a stock can fluctuate daily, and it’s influenced by various factors like company performance, economic conditions, and investor sentiment. Companies can also issue dividends, which are payments made to shareholders from the company’s profits.
Types of Stocks
There are two main types of stocks: common stocks and preferred stocks.
- Common Stocks: These are the most common type of stock, and they give you voting rights in the company. This means you can have a say in major decisions, such as electing the board of directors. Common stock prices are more volatile than preferred stocks, but they have the potential for higher returns.
- Preferred Stocks: These stocks have priority over common stocks in terms of dividends and asset distribution if a company goes bankrupt. They usually don’t have voting rights, but they offer a more stable income stream than common stocks.
The Stock Market and Its Key Players
The stock market is a complex system with many players, including:
- Investors: Individuals and institutions who buy and sell stocks, hoping to make a profit.
- Brokers: Financial professionals who help investors buy and sell stocks, providing advice and executing trades.
- Exchanges: Organized marketplaces where stocks are traded, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq Stock Market.
- Regulators: Government agencies, like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), that oversee the stock market and protect investors from fraud.
Setting Investment Goals and Strategy
Investing in the stock market is a journey, and like any journey, it’s essential to have a destination in mind. Defining your investment goals and understanding your risk tolerance are crucial first steps.
Defining Investment Goals
Your investment goals are the specific financial objectives you aim to achieve through investing. These goals can be short-term, such as saving for a down payment on a house within the next few years, or long-term, like funding your retirement decades from now. Clearly defined goals provide direction and motivation, helping you stay focused on your investment strategy.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to your capacity and willingness to accept potential losses in pursuit of higher returns. Individuals with a high risk tolerance are comfortable with volatile investments that may fluctuate significantly in value. Those with a low risk tolerance prefer investments that are considered safer, even if they offer lower potential returns. Understanding your risk tolerance helps you choose investments that align with your comfort level and financial situation.
Investment Strategies
Investment strategies are the specific approaches you take to achieve your investment goals. They can be categorized as either long-term or short-term.
Long-Term Investment Strategies
Long-term investment strategies focus on building wealth over an extended period, typically several years or decades. These strategies often involve investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other assets. Long-term investors generally have a higher risk tolerance, as they can weather market fluctuations and benefit from the power of compounding over time. Here are some examples of long-term investment strategies:
- Buy-and-hold: This strategy involves purchasing stocks or other assets and holding them for an extended period, typically years or decades. It is based on the belief that over time, the market will rise, and the value of your investments will increase.
- Value investing: This strategy focuses on identifying undervalued stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value. Value investors believe that these stocks are likely to appreciate in value as the market recognizes their true worth.
- Growth investing: This strategy targets companies that are expected to grow rapidly in the future. Growth investors are willing to pay a premium for these companies, hoping to benefit from their future expansion.
Short-Term Investment Strategies, How to invest in stock
Short-term investment strategies focus on generating profits within a shorter time frame, typically months or even days. These strategies often involve more active trading and speculation, and they can be more risky than long-term strategies. Here are some examples of short-term investment strategies:
- Day trading: This strategy involves buying and selling stocks within the same trading day, attempting to profit from short-term price fluctuations. It requires a high level of skill and market knowledge.
- Swing trading: This strategy involves holding stocks for a few days or weeks, hoping to capitalize on price swings or trends. It requires a more nuanced understanding of technical analysis and market patterns.
- Scalping: This strategy involves making multiple small trades over a short period, aiming to profit from tiny price movements. It is a highly aggressive strategy that requires a significant amount of capital and trading expertise.
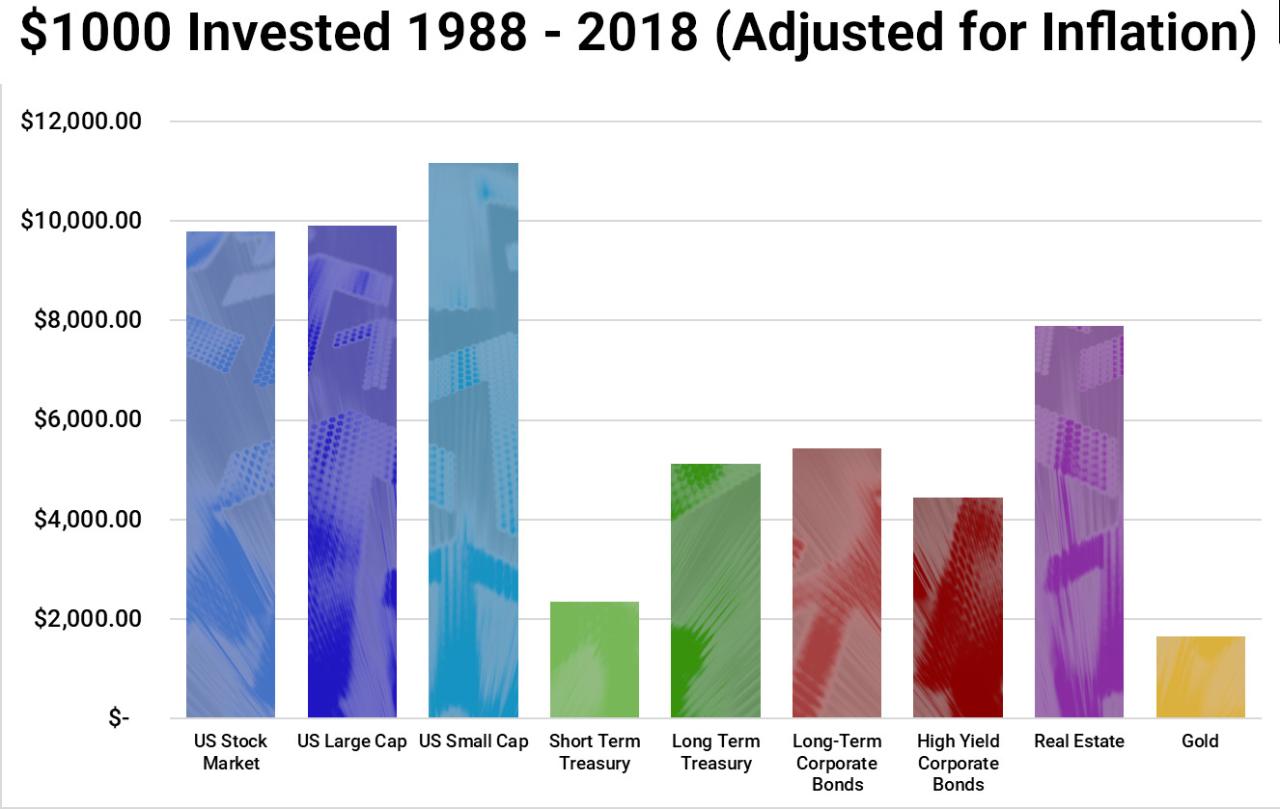
Diversification
Diversification is a key principle in investing that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographies. By diversifying your portfolio, you reduce your overall risk. If one investment performs poorly, other investments may offset those losses. Diversification can be achieved by investing in a variety of stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and other assets.
Diversification is a key risk management strategy in investing. It helps to reduce the overall risk of your portfolio by spreading your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographies.
Research and Analysis

You’ve got your investment goals and strategy, but now you need to know how to pick the right stocks. This is where research and analysis come in. It’s like being a detective, but instead of solving crimes, you’re trying to find companies with the potential to grow your money.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is like digging deep into a company’s financials to see how healthy it is. It helps you understand a company’s performance and its potential for future growth.
- Earnings per share (EPS): This tells you how much profit a company makes for each share of stock. A higher EPS generally indicates a more profitable company.
- Price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio): This compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio can mean investors are willing to pay a premium for the stock, which might indicate high growth potential.
- Debt-to-equity ratio: This shows how much debt a company has compared to its equity. A high ratio could indicate a company is taking on too much risk.
- Return on equity (ROE): This measures how effectively a company is using its shareholders’ investments to generate profits. A higher ROE is generally better.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on patterns and trends in stock prices, using charts and other tools to predict future movements. Think of it like reading tea leaves, but for stocks.
- Moving averages: These lines on a chart show the average price of a stock over a specific period. They can help identify trends and potential support or resistance levels.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): This indicator measures how quickly a stock price is moving up or down. A high RSI can indicate a stock is overbought, while a low RSI might mean it’s oversold.
- Chart patterns: Some patterns on stock charts can suggest potential price movements. For example, a “head and shoulders” pattern might indicate a reversal in the trend.
Choosing a Brokerage Account: How To Invest In Stock
You’ve decided to dive into the world of investing, and now it’s time to choose a brokerage account. This is the platform where you’ll buy and sell stocks, and it’s crucial to pick one that fits your needs and investment goals.
Types of Brokerage Accounts
Let’s break down the different types of brokerage accounts available.
- Traditional Brokerage Accounts: These are your classic, full-service brokerage accounts, often offered by large financial institutions. They provide personalized advice and guidance, but come with higher fees. Think of it like having a financial advisor by your side, but at a cost.
- Online Brokerage Accounts: These are the go-to for many investors, offering lower fees and easy-to-use platforms. You’re in charge of your own investments, but you’ll have access to a wealth of online resources and research tools. Think of it like having a self-service supermarket, where you pick and choose what you want.
- Robo-Advisors: These are automated investment platforms that use algorithms to create and manage your portfolio. They’re ideal for hands-off investors who want to set it and forget it. Think of it like a robotic chef that prepares your meals based on your preferences.
Key Features to Consider
Choosing the right brokerage account is like picking the right tool for the job. Here are some key features to keep in mind:
- Fees: Fees can vary significantly, so it’s important to compare them across different platforms. Look for accounts with low trading commissions, account maintenance fees, and inactivity fees.
- Trading Platforms: The trading platform is your interface for buying and selling stocks. It should be user-friendly and offer the features you need, such as real-time quotes, charting tools, and order types.
- Research Tools: Access to research and analysis can be invaluable for making informed investment decisions. Look for platforms that offer stock reports, analyst ratings, and news feeds.
- Customer Support: Having reliable customer support is essential, especially if you’re a beginner. Choose a platform with responsive phone, email, and chat support.
Reputable Brokerage Platforms for Beginners
- Fidelity: Known for its low fees, user-friendly platform, and excellent customer support. It’s a great option for both beginners and experienced investors.
- Vanguard: A pioneer in index funds and ETFs, Vanguard offers a range of low-cost investment options and a straightforward platform. It’s a solid choice for long-term investors.
- Charles Schwab: Offers a robust platform with a wide selection of investment products and research tools. It’s a good choice for investors who want a comprehensive experience.
- Robinhood: A popular choice for younger investors, Robinhood offers commission-free trading and a user-friendly mobile app. It’s a good option for those who are just starting out.
Last Word

Investing in the stock market can be a rewarding experience, but it’s important to remember that it’s a long-term game. Don’t expect to get rich quick, and be prepared for ups and downs along the way. By following the advice in this guide and doing your research, you can set yourself up for success in the stock market.
Q&A
What is the best time to invest in the stock market?
There’s no single best time to invest. The stock market fluctuates constantly, so it’s generally recommended to invest regularly, regardless of market conditions. This approach, known as dollar-cost averaging, helps to reduce the impact of market volatility.
How much money do I need to start investing?
You can start investing with as little as a few dollars. Many brokerage accounts allow you to invest in fractional shares, meaning you can buy a portion of a stock rather than the whole share.
Is it safe to invest in stocks?
Investing in stocks involves risk, as the value of your investments can go up or down. However, over the long term, the stock market has historically delivered positive returns. It’s important to diversify your portfolio and invest for the long haul to minimize risk.





