
Imagine a world where plugging in your phone in another country means risking a fried device or a fire. Thankfully, that’s not the reality thanks to international electricity standards. These standards, a complex web of regulations and guidelines, ensure that electrical devices and systems can seamlessly connect and operate across borders, facilitating global trade, fostering technological advancement, and ultimately powering our interconnected world.
The history of international electricity standards is a fascinating journey marked by innovation, collaboration, and a constant drive for safety and efficiency. From the early days of the telegraph to the modern era of smart grids, these standards have evolved to accommodate technological advancements and address emerging challenges. They have become the cornerstone of a global energy infrastructure, ensuring the smooth flow of power and enabling the widespread adoption of electrical technologies.
Introduction
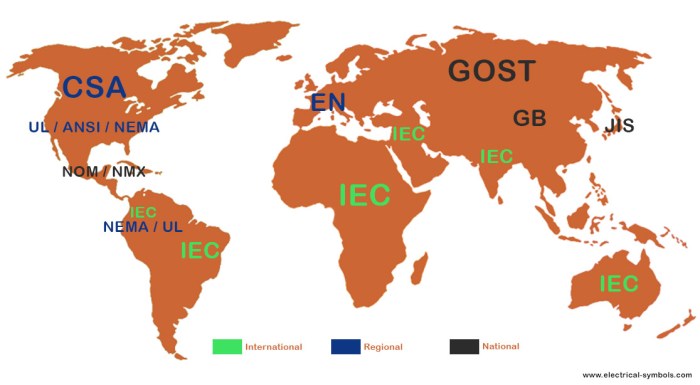
In today’s interconnected world, electricity plays a vital role in powering our lives and driving economic growth. International electricity standards are essential for ensuring the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of electrical systems across borders. These standards facilitate global trade in electrical equipment and promote cooperation among nations in the development and deployment of new technologies.
Historical Development of International Electricity Standards
The development of international electricity standards has a long and rich history, reflecting the evolution of electrical technology itself. Early efforts to standardize electrical systems began in the late 19th century, with the emergence of national standards organizations in various countries.
- In 1906, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) was founded to address the growing need for international cooperation in the field of electrical engineering. The IEC, headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a global organization that brings together experts from over 100 countries to develop and promote international standards for electrical and electronic technologies.
- Over the years, the IEC has developed a comprehensive set of standards covering various aspects of electricity, including voltage, frequency, connectors, and safety requirements. These standards have played a crucial role in enabling the global trade of electrical equipment and ensuring the compatibility of electrical systems across different regions.
Major International Organizations Involved in Setting and Promoting Electricity Standards
Several international organizations, in addition to the IEC, are actively involved in setting and promoting electricity standards:
- The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is another key player in the field of standardization, focusing on a wide range of industries, including electricity. ISO works closely with the IEC to ensure that their standards are aligned and complementary.
- Regional organizations, such as the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), also play a significant role in developing and promoting electricity standards within their respective regions.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA), a global energy organization, works with its member countries to promote energy security, efficiency, and sustainability. The IEA provides guidance on electricity standards and promotes the adoption of best practices for energy systems.
Key Aspects of International Electricity Standards

International electricity standards are crucial for ensuring compatibility, safety, and efficiency in the global electrical system. They encompass a wide range of specifications that govern various aspects of electrical infrastructure, devices, and practices.
Categories of International Electricity Standards
International electricity standards cover a wide range of aspects, including:
- Voltage and Frequency: These standards define the voltage and frequency of electrical power supplied in different regions. For instance, most of North America operates on a 120-volt, 60-Hz system, while Europe uses a 230-volt, 50-Hz system.
- Plug Types and Sockets: These standards dictate the shape and configuration of electrical plugs and sockets, ensuring compatibility between devices and power outlets. Different countries have adopted unique plug types, such as the Type A plug used in North America and the Type C plug used in Europe.
- Safety Regulations: These standards set guidelines for electrical safety, covering aspects like insulation, grounding, and overcurrent protection. They aim to minimize the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and other hazards.
- Wiring and Installation Practices: These standards define the methods and materials used for wiring and installing electrical systems. They ensure safe and reliable electrical connections within buildings and infrastructure.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): These standards address the compatibility of electrical devices with each other and their surrounding environment. They aim to minimize interference between devices and ensure their proper functioning.
Benefits of International Electricity Standards
Adhering to international electricity standards offers numerous benefits for manufacturers, consumers, and economies:
- Enhanced Interoperability: Standardized electrical systems allow devices from different manufacturers to operate seamlessly in various regions. This fosters global trade and reduces the need for region-specific modifications.
- Improved Safety: International safety standards ensure that electrical products meet minimum safety requirements, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. They also promote the development of safer electrical infrastructure.
- Reduced Costs: Standardization simplifies manufacturing processes, reduces the need for multiple product variations, and minimizes testing and certification requirements, ultimately leading to lower costs for manufacturers and consumers.
- Increased Efficiency: International standards promote the adoption of efficient electrical technologies and practices, leading to reduced energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Facilitated Economic Growth: Harmonized electricity standards foster international trade and investment, contributing to economic growth and development.
Challenges of Harmonizing Electricity Standards
While the benefits of international electricity standards are significant, harmonizing them across different regions and countries presents challenges:
- Historical Practices: Different regions have developed unique electrical systems based on historical factors, making it challenging to adopt universal standards. For example, the US and Canada continue to use a 120-volt system, while most other countries use a 230-volt system.
- Political and Economic Interests: National interests and economic considerations can sometimes hinder the adoption of international standards. Governments and industries may prioritize their own standards or resist changes that might disrupt existing systems.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements can lead to the emergence of new standards and create conflicts with existing ones. For instance, the development of renewable energy technologies has prompted the need for new standards for grid integration and energy storage.
Final Wrap-Up

International electricity standards are more than just technical guidelines; they are the invisible threads that connect the world’s electrical systems. They promote safety, interoperability, and efficiency, paving the way for a more sustainable and interconnected energy future. As technology continues to evolve and new challenges arise, the role of these standards will become even more critical, ensuring that the global flow of power remains reliable, efficient, and safe for generations to come.
Clarifying Questions
What are the main challenges in harmonizing electricity standards across different regions?
Harmonizing electricity standards across different regions presents several challenges, including differing historical developments, technological preferences, and national interests. Political considerations, economic factors, and the need to balance standardization with innovation also play a role. Overcoming these challenges requires ongoing dialogue, cooperation, and a commitment to finding common ground.
How do international electricity standards impact the global market for electrical equipment and appliances?
International electricity standards create a level playing field for manufacturers by establishing common requirements for product safety, performance, and interoperability. This facilitates global trade, reduces production costs, and enables manufacturers to access a wider market. Consumers benefit from a greater choice of products, improved safety, and greater confidence in the products they purchase.
What are some examples of international organizations involved in setting and promoting electricity standards?
Some prominent international organizations involved in setting and promoting electricity standards include the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These organizations develop and publish standards, facilitate collaboration among stakeholders, and promote the adoption of best practices in the global electrical industry.





