
- International Maritime Law Bill of Lading: A Legal Guide
-
FAQ about International Maritime Law Bill of Lading
- What is a bill of lading?
- What are the key elements of a bill of lading?
- What are the different types of bills of lading?
- What is the purpose of a bill of lading?
- What are the legal implications of a bill of lading?
- What are the international laws governing bills of lading?
- What are the liabilities of the carrier under a bill of lading?
- What are the rights of the shipper under a bill of lading?
- What are the remedies available to shippers and carriers in the event of a breach of contract?
- How can I obtain a copy of a bill of lading?
International Maritime Law Bill of Lading: A Legal Guide
Introduction
Hello readers,
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on international maritime law bills of lading. In this article, we will dive into the intricate world of shipping documents and explore the legal implications of bills of lading. Whether you’re a seasoned shipper or just getting started, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and clarity on this crucial aspect of international maritime trade.
Bill of Lading: A Legal Document
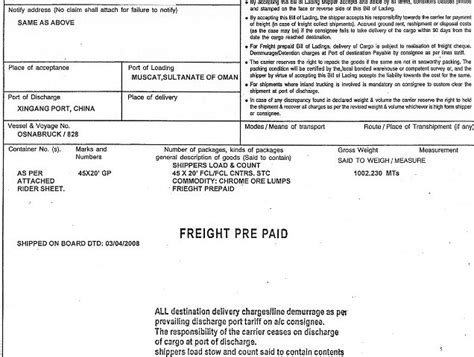
The bill of lading is a fundamental legal document in international maritime law. It serves as a contract between the shipper, carrier, and consignee, outlining the terms and conditions of the shipment. This document acknowledges the receipt of goods by the carrier and obligates them to transport and deliver the goods to the designated consignee. The bill of lading also serves as evidence of ownership of the goods during transit.
Elements of a Bill of Lading
1. Document of Title
The bill of lading is a document of title, meaning that it represents the goods themselves. It grants the holder of the bill of lading the right to take possession of the goods upon delivery.
2. Contract of Carriage
The bill of lading is a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier. It outlines the terms and conditions of the shipment, including the route, delivery timeframe, and payment terms.
3. Evidence of Receipt
The bill of lading serves as evidence that the carrier has received the goods for shipment. It specifies the quantity, weight, and condition of the goods upon receipt.
Significance of Bills of Lading
1. Legality and Customs
Bills of lading are essential for complying with international trade regulations and customs requirements. They facilitate the smooth flow of goods across borders and provide proof of legal ownership during transit.
2. Insurance and Finance
Bills of lading are used as collateral for insurance and financing purposes. They provide evidence of the value and condition of the goods, enabling shippers to obtain insurance and secure financing for their shipments.
3. Risk Allocation
The bill of lading allocates risk and liability between the shipper, carrier, and consignee. It specifies the responsibilities of each party in the event of loss, damage, or delay during transit.
Types of Bills of Lading
1. Straight Bill of Lading
A straight bill of lading is a non-negotiable document that identifies the consignee and entitles them to receive the goods upon delivery.
2. Order Bill of Lading
An order bill of lading is a negotiable document that can be transferred or endorsed to a third party. Whoever holds the order bill of lading has the right to take possession of the goods.
Bill of Lading as a Legal Standard
The bill of lading is a binding legal standard that governs the rights and obligations of the parties involved in the shipment of goods. It is governed by international maritime conventions and national laws, ensuring that the terms and conditions of the contract are enforceable.
Differences between a Charter Party and a Bill of Lading
A charter party is a contract between the ship owner and the charterer, outlining the terms and conditions for the use of the vessel. A bill of lading, on the other hand, is a contract between the shipper and the carrier, covering the terms and conditions of the shipment of goods.
Conclusion
The international maritime law bill of lading is a complex and multifaceted legal document that plays a crucial role in international trade. By understanding the elements, significance, and legal implications of bills of lading, you can ensure the smooth and efficient movement of your goods across international borders.
For further information and insights, we encourage you to explore our other articles on international maritime law and related topics.
FAQ about International Maritime Law Bill of Lading
What is a bill of lading?
A bill of lading is a document that serves as a contract between the shipper of goods and the carrier, usually a shipping company. It is issued by the carrier and contains details about the goods being shipped, such as the type, quantity, and weight, as well as the terms and conditions of the transportation.
What are the key elements of a bill of lading?
The key elements of a bill of lading include the name of the shipper, the name of the carrier, the name of the consignee (the person or company receiving the goods), the description of the goods, the weight and dimensions of the goods, the date and place of shipment, the date and place of delivery, the freight charges, and the terms and conditions of carriage.
What are the different types of bills of lading?
There are two main types of bills of lading: straight bills of lading and negotiable bills of lading. A straight bill of lading is a non-negotiable document that serves as a receipt for the goods, while a negotiable bill of lading can be transferred to a third party, such as a bank, which can then take possession of the goods.
What is the purpose of a bill of lading?
A bill of lading serves several purposes, including providing evidence of the contract of carriage, documenting the condition of the goods at the time of shipment, and providing a record of the goods being transported. It also serves as a legal document that can be used to resolve disputes between shippers and carriers.
What are the legal implications of a bill of lading?
A bill of lading is a legally binding document that creates a contract between the shipper and the carrier. It establishes the rights and obligations of both parties, including the terms of carriage, the liability of the carrier, and the remedies available to the parties in the event of a breach of contract.
What are the international laws governing bills of lading?
The international laws governing bills of lading include the Hague Rules, the Hague-Visby Rules, and the Hamburg Rules. These laws establish uniform rules for the carriage of goods by sea and provide a framework for resolving disputes between shippers and carriers.
What are the liabilities of the carrier under a bill of lading?
The carrier is liable for any loss or damage to the goods that occurs during transportation, unless the loss or damage is caused by an act or omission of the shipper or an inherent defect in the goods. The carrier’s liability is limited by the terms of the bill of lading and the applicable law.
What are the rights of the shipper under a bill of lading?
The shipper has the right to have the goods transported in accordance with the terms of the bill of lading, to receive a copy of the bill of lading, and to file a claim for loss or damage to the goods. The shipper also has the right to inspect the goods before shipment and to make a notation on the bill of lading of any defects or damage.
What are the remedies available to shippers and carriers in the event of a breach of contract?
In the event of a breach of contract, the shipper or carrier may seek legal remedies such as damages, injunctions, or specific performance. The remedies available will depend on the terms of the bill of lading and the applicable law.
How can I obtain a copy of a bill of lading?
You can obtain a copy of a bill of lading from the shipper, the carrier, or the consignee. You can also obtain a certified copy of a bill of lading from the issuing authority.



