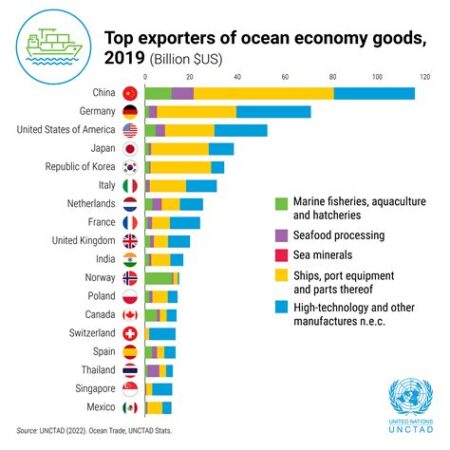
- Introduction
- Regulatory Framework for Maritime Exports
- Legal Obligations of Exporters
-
FAQ about Laws on Maritime Exporting of Commodities
- 1. What is the legal framework governing maritime export of commodities?
- 2. What are the key requirements for exporting commodities by sea?
- 3. Who is responsible for enforcing maritime export laws?
- 4. What are the penalties for violating maritime export laws?
- 5. Are there any special requirements for exporting hazardous or controlled commodities?
- 6. How do I obtain an export license?
- 7. What is the role of a freight forwarder in maritime export?
- 8. What are the different types of shipping vessels used for exporting commodities?
- 9. What are the insurance considerations for maritime export?
- 10. How do I keep up with changes in maritime export laws and regulations?
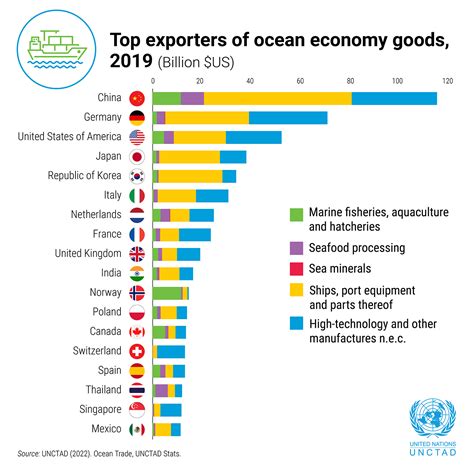
Introduction
Greetings, readers! The maritime industry plays a crucial role in facilitating global trade, and the exportation of commodities via sea routes is a significant aspect of this sector. To ensure the smooth and legal operation of maritime exports, various laws and regulations have been established. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these laws on maritime exporting of commodities, providing a clear understanding of the legal framework governing this important aspect of international commerce.
Regulatory Framework for Maritime Exports
International Conventions
The maritime industry operates under a network of international conventions that set forth standards and guidelines for the safe and efficient movement of goods across borders. These conventions cover various aspects, including:
-
International Maritime Organization (IMO): Established in 1948, the IMO is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for developing and maintaining international standards for maritime safety, environmental protection, and maritime law.
-
World Trade Organization (WTO): The WTO is an intergovernmental organization that establishes rules for international trade, including the movement of goods across borders. The WTO’s General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) provides a framework for reducing trade barriers and promoting fair competition.
National Legislation
In addition to international conventions, individual countries have their own national legislation governing the exportation of commodities via maritime channels. These laws may vary depending on the country’s specific economic policies and trade regulations. Typically, national legislation covers:
-
Export Licensing Requirements: Many countries require exporters to obtain licenses or permits before exporting certain commodities. These licenses may be subject to specific conditions and restrictions, such as export quotas or destination restrictions.
-
Customs Regulations: Customs authorities are responsible for enforcing import and export regulations, including the collection of duties and taxes on exported commodities. Exporters must comply with customs procedures and declarations to facilitate the smooth flow of goods across borders.
Legal Obligations of Exporters
Exporters involved in the maritime export of commodities must adhere to the following legal obligations:
Proper Documentation
Exporters are required to maintain accurate and up-to-date documentation related to their exports. This documentation may include:
-
Bills of lading: These legal documents provide evidence of the contract of carriage between the exporter and the shipping company.
-
Commercial invoices: These invoices detail the goods being exported, their value, and the terms of sale.
-
Certificates of origin: These certificates certify the country of origin of the exported commodities.
Compliance with Export Restrictions
Exporters must comply with any export restrictions or prohibitions imposed by the governments of the exporting or importing countries. These restrictions may be based on factors such as national security, environmental protection, or human rights concerns.
Payment of Duties and Taxes
Exporters are responsible for paying any applicable duties and taxes on exported commodities. These charges may vary depending on the country and the type of commodity being exported.
FAQ about Laws on Maritime Exporting of Commodities
1. What is the legal framework governing maritime export of commodities?
- The legal framework includes national laws, international conventions, and trade agreements that regulate the export of commodities by sea.
2. What are the key requirements for exporting commodities by sea?
- Proper documentation, including export licenses, certificates of origin, and bills of lading. Compliance with customs regulations and payment of applicable duties and taxes.
3. Who is responsible for enforcing maritime export laws?
- Customs authorities, port authorities, and other regulatory agencies are responsible for enforcing these laws.
4. What are the penalties for violating maritime export laws?
- Penalties may include fines, imprisonment, and seizure of goods.
5. Are there any special requirements for exporting hazardous or controlled commodities?
- Yes, additional safety and security measures may be required for the export of hazardous or controlled commodities, such as chemicals, weapons, or radioactive materials.
6. How do I obtain an export license?
- Application for an export license is typically made through the relevant government agency responsible for trade regulation.
7. What is the role of a freight forwarder in maritime export?
- Freight forwarders provide logistical support and documentation for the export process, including booking cargo space, preparing shipping documents, and coordinating with customs authorities.
8. What are the different types of shipping vessels used for exporting commodities?
- Various types of shipping vessels are used, including container ships, bulk carriers, tankers, and specialized vessels for specific commodity types.
9. What are the insurance considerations for maritime export?
- Marine cargo insurance is essential to protect goods from loss, damage, or theft during transit.
10. How do I keep up with changes in maritime export laws and regulations?
- It is important to stay informed by regularly checking government websites, consulting with trade organizations, and attending industry events.