
- Section 1: Introduction to Maritime Law
- Section 2: Key Concepts in Maritime Law
- Section 3: Enforcement and Disputes
- Section 4: Admiralty Law Table Breakdown
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about Maritime Law Basics
- What is maritime law?
- Who has jurisdiction over maritime disputes?
- What is the difference between maritime law and admiralty law?
- What are the main types of maritime law cases?
- What is general average?
- What is salvage?
- What is a maritime lien?
- What is the Limitation of Liability Act?
- What is the Jones Act?
- What is the Death on the High Seas Act (DOHSA)?
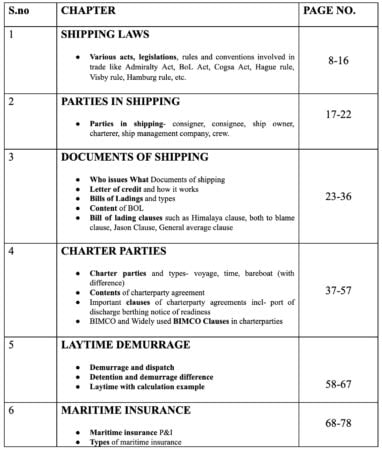
Section 1: Introduction to Maritime Law
Greetings, readers! Welcome to our in-depth guide to maritime law basics, where we’ll dive into the depths of this fascinating legal world governing the oceans and waterways. Maritime law, also known as admiralty law, is a specialized field that deals with legal issues arising from commercial, recreational, and environmental activities at sea. From ship collisions to salvage operations, this realm of law ensures the safe and equitable navigation of our vast maritime realm.
Maritime law plays a vital role in regulating international trade, transportation, and resource exploitation. Its intricate framework encompasses a wide range of areas, including maritime contracts, personal injury claims, vessel registration, and environmental protection. Understanding these basics will equip you with a solid foundation for further exploration into this captivating legal landscape.
Section 2: Key Concepts in Maritime Law
Maritime Contracts
Contracts are the backbone of maritime law, governing everything from ship purchase agreements to cargo carriage contracts. These specialized contracts often involve complex legal principles and international regulations, requiring expert drafting and interpretation.
Personal Injury Claims
Accidents on the high seas can lead to serious injuries, prompting victims to seek compensation. Maritime personal injury law provides a framework for determining liability, damages, and legal remedies.
Vessel Registration
All vessels operating in navigable waters must be registered with the appropriate authority. Maritime law governs vessel registration processes, ensuring compliance with safety standards and ownership documentation requirements.
Environmental Protection
Environmental protection is a growing concern in maritime law as human activities impact the health of our oceans. Laws regulate pollution prevention, waste disposal, and vessel emissions to protect marine ecosystems.
Section 3: Enforcement and Disputes
Admiralty Courts
Specialized admiralty courts handle maritime disputes, offering expertise in this complex field of law. These courts adjudicate cases involving shipwrecks, cargo damage, and international maritime disputes.
Jurisdiction and Choice of Law
Maritime law often involves issues of jurisdiction and choice of law due to the international nature of shipping activities. Courts must determine which laws and courts have authority in a given case.
Enforcement Mechanisms
Enforcement mechanisms in maritime law include in rem actions (actions against vessels) and in personam actions (actions against individuals or corporations). Admiralty courts have unique powers to arrest vessels and seize property to secure claims.
Section 4: Admiralty Law Table Breakdown
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Maritime Contracts | Legal agreements governing ship purchases, cargo carriage, and more |
| Personal Injury Claims | Legal remedies for injuries sustained in maritime accidents |
| Vessel Registration | Process of registering vessels with authorities to ensure compliance and ownership documentation |
| Environmental Protection | Laws regulating pollution prevention and waste disposal to protect marine ecosystems |
| Admiralty Courts | Specialized courts handling maritime disputes with expertise in this field of law |
| Jurisdiction and Choice of Law | Determining applicable laws and courts in maritime disputes |
| Enforcement Mechanisms | Methods to enforce maritime judgments, including in rem and in personam actions |
Conclusion
Our maritime law basics guide has provided an overview of this multifaceted legal landscape, from its key concepts to enforcement mechanisms. Understanding these basics opens a gateway to further exploration of this fascinating and ever-evolving field.
Readers, we encourage you to delve deeper into the world of maritime law by checking out our other articles covering specific aspects of this rich legal domain. Stay tuned for more insights and legal adventures!
FAQ about Maritime Law Basics
What is maritime law?
Maritime law, also known as admiralty law, governs legal issues that arise in connection with the sea, including navigation, shipping, and maritime commerce.
Who has jurisdiction over maritime disputes?
Jurisdiction over maritime disputes generally falls under the authority of courts that have jurisdiction over the waters where the incident occurred. In many cases, federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction over maritime claims arising on navigable waters.
What is the difference between maritime law and admiralty law?
Traditionally, maritime law applied to issues arising within the territorial waters of a nation, while admiralty law applied to issues arising in international waters. However, in practice, the terms are often used interchangeably.
What are the main types of maritime law cases?
Common types of maritime law cases include personal injury (e.g., injuries suffered by seamen), property damage (e.g., damage to ships or cargo), maritime contracts (e.g., breach of charter parties), and maritime insurance disputes (e.g., coverage for marine losses).
What is general average?
General average is a legal principle that requires all parties with an interest in a sea voyage to contribute to the extraordinary expenses incurred to save the voyage from a common peril.
What is salvage?
Salvage is the compensation paid to individuals who voluntarily assist in saving a ship or its cargo from danger or distress at sea.
What is a maritime lien?
A maritime lien is a legal claim against a vessel or other maritime property that secures payment of a debt or obligation related to the vessel or its operation.
What is the Limitation of Liability Act?
The Limitation of Liability Act limits the liability of vessel owners for maritime claims to their interest in the vessel and the pending freight.
What is the Jones Act?
The Jones Act provides a negligence remedy for injured seamen who work on vessels in navigable waters.
What is the Death on the High Seas Act (DOHSA)?
DOHSA provides a wrongful death remedy for families of seamen who die in the course of their employment on vessels in international waters.



