In a world grappling with climate change and energy security concerns, sustainable energy laws have emerged as a crucial tool for fostering a cleaner and more resilient energy landscape. These laws serve as the bedrock for transitioning to a future powered by renewable sources, while also promoting economic growth and environmental protection.
From setting ambitious renewable energy targets to establishing carbon pricing mechanisms, sustainable energy laws encompass a wide range of policy instruments designed to incentivize the adoption of clean technologies and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. This comprehensive approach not only addresses the environmental challenges we face but also unlocks new opportunities for innovation and economic development.
Introduction to Sustainable Energy Laws
Sustainable energy laws are legal frameworks that aim to promote the development and use of renewable energy sources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve energy efficiency. They encompass a wide range of regulations, policies, and incentives designed to guide energy production, consumption, and infrastructure development towards a more sustainable path.
Sustainable energy laws play a crucial role in safeguarding the environment and ensuring energy security for present and future generations. By encouraging the transition to renewable energy sources, these laws help mitigate climate change, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and promote energy independence. They also contribute to economic growth and job creation in the renewable energy sector.
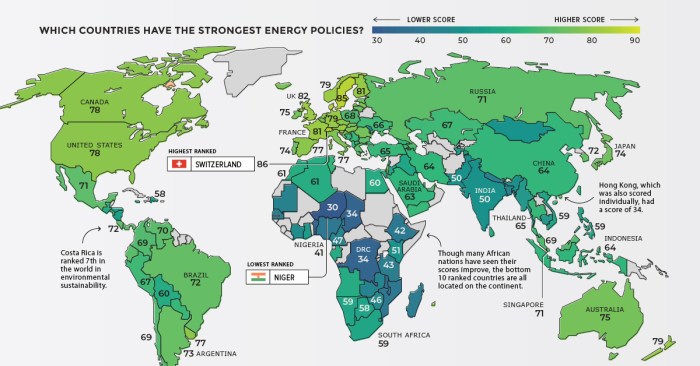
Examples of Countries with Robust Sustainable Energy Laws
Countries with strong sustainable energy laws have made significant progress in transitioning to cleaner energy sources and achieving their climate goals. These laws typically include provisions for renewable energy targets, energy efficiency standards, carbon pricing mechanisms, and support for research and development in sustainable energy technologies.
- Germany: Germany’s Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG) is considered a pioneering example of a sustainable energy law. It has been instrumental in the country’s remarkable success in renewable energy deployment, particularly solar and wind power. The EEG provides guaranteed feed-in tariffs for renewable energy producers, ensuring a stable market for renewable energy investments.
- Denmark: Denmark has a long history of promoting renewable energy, with its wind power sector being a global leader. The country’s sustainable energy laws have played a vital role in this success, including policies that support wind energy development, energy efficiency measures, and carbon taxes.
- China: China, the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases, has implemented ambitious renewable energy targets and policies. The country’s sustainable energy laws include targets for renewable energy deployment, subsidies for renewable energy projects, and regulations on energy efficiency.
Key Elements of Sustainable Energy Laws

Sustainable energy laws are crucial for transitioning to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. These laws aim to promote the development and use of renewable energy sources, enhance energy efficiency, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Key elements of these laws provide a framework for achieving these goals.
Renewable Energy Targets
Renewable energy targets are legally mandated goals for the share of renewable energy in a country’s total energy mix. These targets act as a driving force for investment and innovation in renewable energy technologies. For example, the European Union has set a target of achieving at least 32% of its energy consumption from renewable sources by 2030. These targets incentivize the development of renewable energy infrastructure and encourage businesses and individuals to adopt renewable energy sources.
Energy Efficiency Standards
Energy efficiency standards aim to reduce energy consumption by setting minimum efficiency requirements for appliances, buildings, and industrial processes. These standards encourage manufacturers to produce more energy-efficient products and motivate consumers to choose energy-saving options. For instance, the United States has implemented energy efficiency standards for appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners, leading to significant energy savings.
Carbon Pricing Mechanisms
Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, place a financial cost on carbon emissions. This economic incentive encourages businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint by switching to cleaner energy sources or adopting energy-efficient practices. For example, the European Union’s Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) sets a cap on greenhouse gas emissions from certain industries, requiring them to purchase permits for their emissions.
Examples of Sustainable Energy Laws
| Country | Law | Key Elements |
|—|—|—|
| United States | Clean Air Act (1970) | Sets air quality standards, including regulations for emissions from power plants and other industries. |
| European Union | Renewable Energy Directive (2009) | Sets binding targets for the share of renewable energy in each member state’s energy mix. |
| China | Renewable Energy Law (2005) | Promotes the development of renewable energy, including wind, solar, and biomass. |
| India | National Solar Mission (2010) | Aims to achieve 100 GW of solar power capacity by 2022. |
Final Thoughts
As we navigate the complexities of a changing climate, sustainable energy laws play a pivotal role in guiding us towards a sustainable future. By embracing a holistic approach that encompasses technological advancements, policy innovation, and public engagement, we can unlock the full potential of clean energy and build a world that is both prosperous and environmentally responsible. The future of energy is undeniably green, and sustainable energy laws are the roadmap to get us there.
Q&A
What are the main benefits of sustainable energy laws?
Sustainable energy laws offer numerous benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, increased energy security, and economic growth through the creation of new jobs and industries.
How do sustainable energy laws impact the economy?
Sustainable energy laws stimulate economic growth by fostering innovation in clean technologies, creating jobs in the renewable energy sector, and reducing energy costs through efficiency measures.
What are the challenges in implementing sustainable energy laws?
Challenges include the need for significant upfront investment, potential resistance from traditional energy industries, and the need for robust infrastructure development to support renewable energy sources.
How can public acceptance of sustainable energy laws be increased?
Public acceptance can be enhanced through transparent communication, education campaigns, and showcasing the tangible benefits of clean energy, such as improved air quality and reduced energy bills.