
What is civil law? It’s a legal system that governs many countries around the world, shaping everything from contracts and property ownership to family matters and personal injury cases. Unlike common law systems, which rely heavily on precedent, civil law systems are built on comprehensive, codified laws. Think of it as a detailed legal blueprint that lays out the rules for society.
Understanding the core principles of civil law is crucial for anyone interested in law, international relations, or simply navigating the legal landscape of a civil law jurisdiction. This system, rooted in Roman law, has a rich history and continues to evolve in response to modern challenges.
Definition of Civil Law: What Is Civil Law
Civil law, also known as Roman law, is a legal system that is based on codified statutes and legislation. It is characterized by its emphasis on written laws, which are applied and interpreted by judges to resolve disputes. This system contrasts with common law, where judicial precedents play a significant role in shaping the law.
Core Principles of Civil Law
Civil law systems adhere to a set of core principles that guide their legal frameworks. These principles ensure consistency and predictability in the application of the law.
- Codification: Civil law systems are based on comprehensive legal codes that systematically organize and codify the law. These codes serve as the primary source of law and provide a comprehensive framework for legal decision-making.
- Statutory Interpretation: Judges in civil law systems primarily interpret and apply the existing codified law. They are bound by the provisions of the legal codes and are expected to adhere to the literal meaning of the law.
- Inquisitorial System: Civil law systems often employ an inquisitorial system of justice, where the judge plays an active role in investigating and gathering evidence. This contrasts with the adversarial system of common law, where the parties present their own evidence and arguments.
- Emphasis on Written Law: Civil law systems prioritize written law as the primary source of legal authority. Judges are expected to base their decisions on the codified statutes and legal principles established in the codes.
Comparison with Common Law
Civil law and common law systems differ significantly in their approaches to legal decision-making.
- Source of Law: Civil law relies primarily on codified statutes, while common law emphasizes judicial precedents, known as case law.
- Role of Judges: In civil law systems, judges are primarily interpreters of the law, while in common law systems, judges have the power to create new law through their decisions.
- Legal Process: Civil law systems often employ an inquisitorial process, where the judge is actively involved in investigating and gathering evidence. Common law systems, on the other hand, use an adversarial process, where the parties present their own evidence and arguments.
- Legal Education: Civil law education focuses on legal theory and the application of codified law. Common law education emphasizes case analysis and the development of legal reasoning skills.
Examples of Legal Codes
Numerous countries worldwide operate under civil law systems, each with its own unique legal code. Here are some notable examples:
- French Civil Code (Code Civil): This code, enacted in 1804, is considered a landmark achievement in legal history and has influenced legal systems across the globe. It covers a wide range of legal areas, including family law, property law, and contracts.
- German Civil Code (BGB): The BGB, enacted in 1900, is another influential civil code that has served as a model for other legal systems. It is known for its systematic structure and comprehensive coverage of legal principles.
- Swiss Civil Code (ZGB): The ZGB, enacted in 1907, is a relatively concise code that is renowned for its clarity and comprehensiveness. It is a highly influential code that has been adopted by several other countries.
Sources of Civil Law
Civil law, as a legal system, has its roots in ancient Roman law. This system has evolved over centuries, influenced by various historical, social, and political factors. Understanding the sources of civil law is crucial for grasping its principles, development, and application in modern legal systems.
Historical Origins of Civil Law
The foundation of civil law lies in the Roman legal system, specifically in the *Corpus Juris Civilis*, compiled under the reign of Emperor Justinian in the 6th century AD. This comprehensive collection of Roman law served as a cornerstone for the development of civil law in Europe and beyond. It encompassed various legal sources, including:
- The Twelve Tables: This ancient code, dating back to the 5th century BC, established fundamental legal principles and procedures, laying the groundwork for Roman law.
- Edicts of the Praetors: Roman magistrates known as praetors issued edicts, which were pronouncements on legal matters that evolved over time and contributed to the growth of Roman law.
- Writings of Roman Jurists: Prominent legal scholars like Gaius, Papinian, and Ulpian wrote extensively on legal topics, providing interpretations and analyses that influenced Roman law development.
- Imperial Decrees: Roman emperors issued decrees that addressed specific legal issues, adding to the body of Roman law.
Key Legal Scholars and Their Contributions
Several legal scholars played pivotal roles in shaping civil law throughout history. Their contributions ranged from codifying existing law to introducing new legal concepts and interpretations. Here are some notable figures:
- Justinian I: This Byzantine emperor commissioned the compilation of the *Corpus Juris Civilis*, a monumental work that preserved and systematized Roman law, making it accessible to future generations.
- Bartolus de Sassoferrato: A 14th-century Italian jurist, he was a prominent legal scholar who provided influential interpretations of Roman law, particularly in the field of contract law.
- Hugo Grotius: A 17th-century Dutch jurist, he is known for his contributions to natural law and international law, advocating for universal principles of justice and human rights.
- Friedrich Carl von Savigny: A 19th-century German jurist, he emphasized the historical development of law and the importance of legal tradition in shaping legal systems. His work contributed to the revival of Roman law in Germany.
Role of Legislation, Judicial Precedent, and Legal Scholarship, What is civil law
Civil law systems are primarily characterized by their reliance on legislation as the primary source of law. This means that laws are codified in written statutes, which are enacted by legislatures. However, other sources also play significant roles in shaping civil law:
- Legislation: This is the most prominent source of law in civil law systems. Statutes, or codes, provide a comprehensive framework for legal rules and principles, covering a wide range of legal areas, from criminal law to family law to property law.
- Judicial Precedent: While civil law systems do not strictly adhere to the doctrine of *stare decisis* (binding precedent), judicial decisions can influence subsequent cases and provide guidance for interpretation of legal provisions. This is particularly true in countries with a long history of civil law, where judicial interpretations have established a body of jurisprudence that complements legislation.
- Legal Scholarship: Legal scholars play a crucial role in analyzing, interpreting, and critiquing legal principles and doctrines. Their writings, often published in academic journals or treatises, contribute to the development of legal theory and practice. They also influence legal education and the training of future legal professionals.
Key Features of Civil Law

Civil law systems are characterized by a distinct set of features that differentiate them from other legal systems, such as common law. These features shape the structure, application, and interpretation of law within these systems.
Key Features of Civil Law
The primary features of civil law systems can be summarized as follows:
| Feature | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Codified Law | Civil law systems rely heavily on comprehensive written codes that establish a comprehensive framework for legal rules and principles. These codes are considered the primary source of law, and judges are bound to apply the codified provisions to specific cases. | The French Civil Code (Code Civil) is a classic example of a codified law system, which establishes fundamental principles for areas such as property, contracts, and family law. |
| Inquisitorial System | In civil law proceedings, the judge plays a more active role in investigating the case and gathering evidence. Unlike the adversarial system of common law, the judge is responsible for directing the investigation and questioning witnesses. | In a French criminal trial, the judge is responsible for leading the investigation, examining witnesses, and presenting evidence to the court. |
| Emphasis on Legal Scholarship | Legal scholarship plays a significant role in interpreting and applying the law in civil law systems. Scholars and legal experts contribute to the development and refinement of legal doctrines through academic writings, commentaries, and treatises. | The works of legal scholars like Émile Durkheim and Montesquieu have significantly influenced the development and interpretation of French law. |
| Formalistic Approach | Civil law systems often adopt a formalistic approach to legal reasoning, emphasizing the strict application of legal rules and principles. Judges are expected to follow established precedents and apply the law consistently. | In a German court, a judge may strictly adhere to the provisions of the German Civil Code (BGB) when deciding a contract dispute. |
Codified Law
Codified law is a fundamental characteristic of civil law systems. It refers to the practice of organizing and systematizing legal rules into comprehensive written codes. These codes are considered the primary source of law, providing a comprehensive framework for legal principles and procedures.
“The codification of law is the process of systematically organizing and writing down the laws of a country or jurisdiction into a comprehensive set of codes.”
The significance of codified law in civil law systems lies in its ability to:
* Provide clarity and certainty: Codified laws offer a clear and concise statement of legal rules, reducing ambiguity and uncertainty in the legal system.
* Ensure consistency and predictability: By establishing a comprehensive framework, codified law promotes consistency in legal decisions and fosters predictability in legal outcomes.
* Promote accessibility and transparency: Codified laws are publicly accessible, making it easier for individuals to understand their legal rights and obligations.
Role of Legal Professionals
Legal professionals play distinct roles in civil law proceedings, contributing to the efficient administration of justice.
* Judges: Judges in civil law systems are responsible for applying the codified law to specific cases. They act as impartial arbiters, interpreting the law and making decisions based on the established legal framework.
* Lawyers: Lawyers in civil law systems primarily advise clients on legal matters, representing them in court proceedings. They are responsible for preparing legal arguments, presenting evidence, and advocating for their clients’ interests.
* Notaries: Notaries play a crucial role in civil law systems, primarily focusing on legal formalities and documentation. They are authorized to authenticate documents, witness legal transactions, and provide legal advice on matters related to contracts, property, and inheritance.
Civil Law in Practice
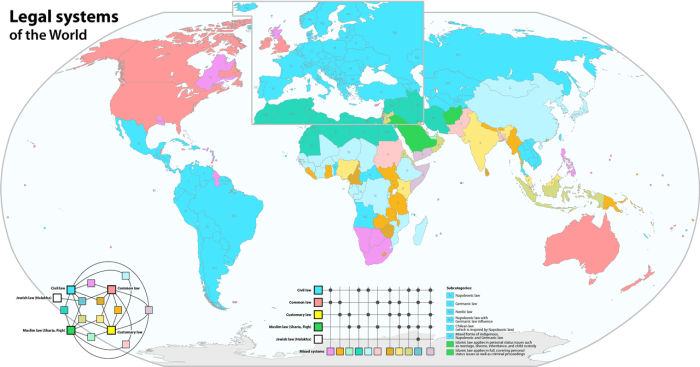
Civil law principles are not merely theoretical constructs; they are the foundation of legal systems that govern daily life in many parts of the world. This section delves into how these principles are applied in various contexts, showcasing their impact on individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
Real-World Applications of Civil Law
Civil law principles are woven into the fabric of everyday life, influencing a wide range of interactions and transactions. Here are some examples:
- Contract Law: When you buy a product online, sign a lease agreement for your apartment, or enter into a business partnership, you are engaging with contract law. Civil law principles define the elements of a valid contract, determine the rights and obligations of parties involved, and provide a framework for resolving disputes that may arise.
- Property Law: Civil law principles govern ownership, use, and transfer of property, whether it’s your home, a piece of land, or intellectual property rights. These principles define how property is acquired, protected, and passed on to future generations.
- Family Law: Civil law principles guide the legal framework for marriage, divorce, child custody, and inheritance. They provide a structure for resolving family disputes and ensuring the well-being of children and spouses.
- Torts: Civil law principles are applied in tort law, which deals with civil wrongs that cause harm to individuals. This includes negligence, intentional torts like battery and defamation, and product liability.
Role of Civil Law in Dispute Resolution and Justice
Civil law plays a crucial role in resolving disputes and upholding justice. It provides a framework for:
- Fair and impartial adjudication: Civil law emphasizes due process and the right to a fair hearing. Courts are tasked with impartially applying legal principles to resolve disputes based on evidence and legal arguments.
- Compensation for harm: Civil law provides mechanisms for individuals to seek compensation for harm caused by others, such as damages for personal injury, property damage, or breach of contract.
- Deterrence of wrongdoing: The threat of legal action and potential financial penalties serves as a deterrent against wrongful conduct, encouraging individuals and businesses to act responsibly.
Illustrative Civil Law Case
A homeowner, Ms. Smith, hired a contractor, Mr. Jones, to renovate her kitchen. Mr. Jones failed to complete the renovation on time and within the agreed-upon budget, leaving Ms. Smith with a partially finished kitchen and significant financial losses. Ms. Smith filed a civil lawsuit against Mr. Jones, alleging breach of contract and negligence. The court, applying principles of contract law and tort law, found in favor of Ms. Smith. Mr. Jones was ordered to pay damages to Ms. Smith for the cost of completing the renovation and for the inconvenience caused by the delay.
Final Wrap-Up
From the historical origins of civil law to its application in contemporary society, we’ve explored the key features and areas of this influential legal system. By understanding the principles of civil law, we gain a deeper appreciation for how laws are made, interpreted, and enforced in a significant portion of the world. Whether you’re a legal professional, a student, or simply curious about the world around you, delving into the world of civil law can provide valuable insights and a broader perspective on the complexities of our legal systems.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between civil law and criminal law?
Civil law deals with disputes between individuals or entities, while criminal law deals with offenses against the state.
What are some examples of countries that use civil law systems?
Many countries in Europe, Latin America, Asia, and Africa use civil law systems, including France, Germany, Italy, Spain, China, and Brazil.
How does civil law impact everyday life?
Civil law influences how we buy and sell goods, own property, resolve family disputes, and interact with businesses and the government.
What are the advantages of a civil law system?
Advantages include a more predictable and consistent legal system, a focus on written law, and a greater emphasis on efficiency in legal proceedings.
Is civil law a better system than common law?
Both civil and common law systems have their strengths and weaknesses. The best system depends on the specific needs and values of a society.




