Introduction
Hi there, readers! Forex, the foreign exchange market, is a vast and exciting world where currencies are traded around the clock. As you dive into this realm, you’ll encounter a fundamental concept known as the spread. Understanding spreads is crucial for successful forex trading, so let’s delve into its intricacies together.
What is Spread in Forex?
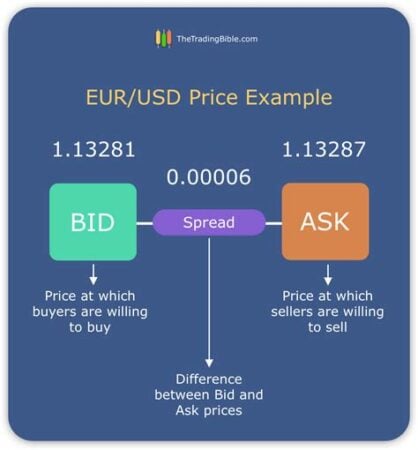
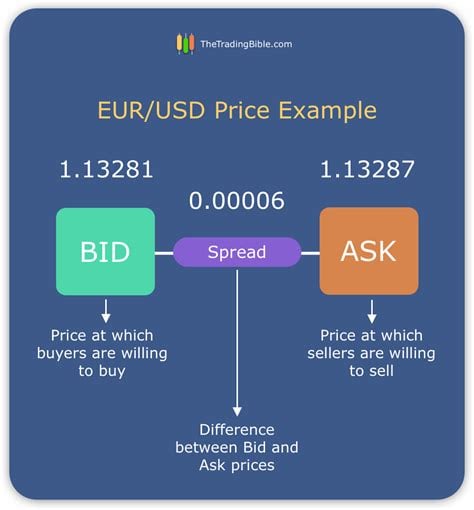
Simply put, the spread in forex is the difference between the bid and ask prices of a currency pair. The bid price is the price at which you can sell a currency, while the ask price is the price at which you can buy it. The spread represents the markup or commission charged by the broker for facilitating the trade.
Types of Spreads in Forex
Fixed Spreads
Fixed spreads, as the name suggests, remain constant regardless of market conditions. They are typically offered by market makers, who quote both the bid and ask prices and assume the other side of the trade. Fixed spreads provide traders with stability and predictability in their trading costs.
Variable Spreads
Variable spreads fluctuate based on market conditions, such as liquidity and volatility. They are generally lower than fixed spreads during periods of high liquidity but can widen significantly during times of low liquidity or high volatility. Variable spreads are often offered by ECN (Electronic Communication Network) brokers, which connect traders directly to liquidity providers.
Factors Affecting Spreads in Forex
Currency Pair Traded
The spread varies depending on the currency pair being traded. Major currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD typically have tighter spreads due to their high liquidity. On the other hand, exotic currency pairs, such as USD/SGD or GBP/PLN, tend to have wider spreads due to their lower liquidity.
Time of Day
Spreads can also vary depending on the time of day. During peak trading hours, liquidity is typically higher, leading to tighter spreads. Conversely, during off-peak hours or weekends, liquidity may be lower, resulting in wider spreads.
Market Volatility
Market volatility plays a significant role in determining spreads. During periods of high volatility, spreads tend to widen as liquidity may decrease and market makers adjust their quotes to manage risk.
Calculating Forex Spreads
To calculate the spread in forex, simply subtract the bid price from the ask price. For example, if the bid price for EUR/USD is 1.1100 and the ask price is 1.1102, the spread would be 2 pips (points).
Impact of Spreads on Forex Trading
Profitability
Spreads can significantly impact your trading profitability. Tighter spreads allow you to enter and exit trades at more favorable prices, reducing your trading costs and increasing your potential profits. Wider spreads, on the other hand, can erode your profits and make it more challenging to achieve a positive trading outcome.
Trading Strategy
The spread can also influence your trading strategy. If you trade high-frequency strategies with small profit margins, it is crucial to minimize spreads to maximize your profits. Similarly, if you trade long-term strategies with larger profit targets, wider spreads may be less impactful on your overall profitability.
Table Breakdown: Forex Spreads
| Type of Spread | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Spread | Stable and predictable | Can be higher than variable spreads |
| Variable Spread | Lower during high liquidity | Can widen significantly during low liquidity or high volatility |
| Raw Spread | Lowest spreads available | May include additional commissions |
Conclusion
Understanding spreads in forex is fundamental for successful trading. By considering the different types of spreads, factors affecting them, and their impact on your trading, you can optimize your strategies and make informed decisions that ultimately enhance your trading performance.
If you’re interested in learning more about forex trading or other financial topics, be sure to check out our other articles!
FAQ about Spreads in Forex
What is a spread in forex?
A spread is the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell a currency pair) and the ask price (the price at which you can buy a currency pair). The spread is usually expressed in pips, which are the smallest unit of price movement in a currency pair.
Why do spreads exist?
Spreads exist because market makers need to make a profit. They quote two prices for a currency pair, one that they are willing to sell at and one that they are willing to buy at. The difference between these two prices is the spread. Market makers make a profit by buying at the bid price and selling at the ask price.
What is the average spread?
The average spread varies depending on the currency pair and the market conditions. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, typically have lower spreads than minor currency pairs. Spreads also tend to be wider during periods of high volatility.
What factors affect the spread?
The spread can be affected by a number of factors, including:
- Market liquidity: The more liquid a currency pair is, the tighter the spread will be.
- Volatility: Spreads tend to be wider during periods of high volatility.
- News events: Major news events can cause spreads to widen.
- Time of day: Spreads tend to be wider during off-peak trading hours.
How can I reduce the impact of spreads?
There are a few things you can do to reduce the impact of spreads on your trading:
- Trade during peak trading hours: Spreads are typically tighter during peak trading hours.
- Choose liquid currency pairs: Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, typically have lower spreads.
- Use a broker with low spreads: Some brokers offer lower spreads than others.
Are spreads fixed?
No, spreads are not fixed. They can change constantly, depending on the market conditions.
Is it possible to profit from spreads?
Yes, it is possible to profit from spreads. However, it is important to remember that spreads are a cost of trading. You need to factor them into your trading strategy and make sure that you have a positive expectancy.
What is a spread bet?
A spread bet is a type of financial bet where you bet on the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair. Spread bets are typically used by short-term traders.
What is a no-spread account?
A no-spread account is a type of trading account that does not charge a spread on trades. No-spread accounts are typically offered by brokers that make their money from other sources, such as commissions.