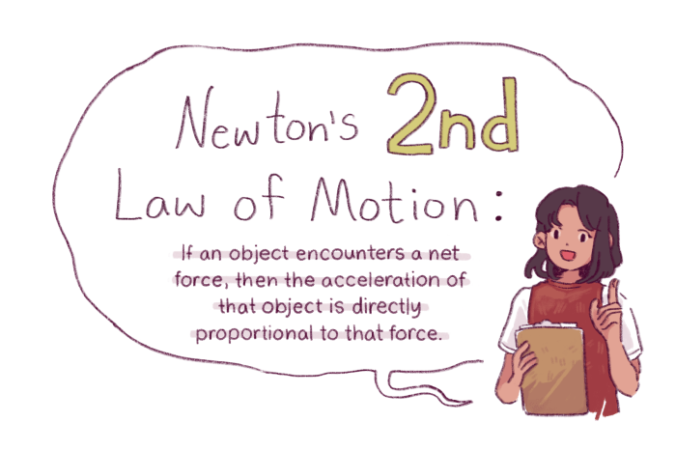
What is the 2nd Law of Motion? This fundamental principle, a cornerstone of physics, governs the motion of objects in the universe. It was formulated by Sir Isaac Newton, a brilliant scientist who revolutionized our understanding of the physical world. This law describes the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration, providing a framework for understanding how objects move and interact.
Imagine pushing a shopping cart. The harder you push (force), the faster it accelerates. Now imagine pushing a heavy box versus a light one with the same force. The heavier box accelerates less. This illustrates the fundamental concepts of force, mass, and acceleration that are at the heart of Newton’s Second Law of Motion.
Introduction to Newton’s Laws of Motion
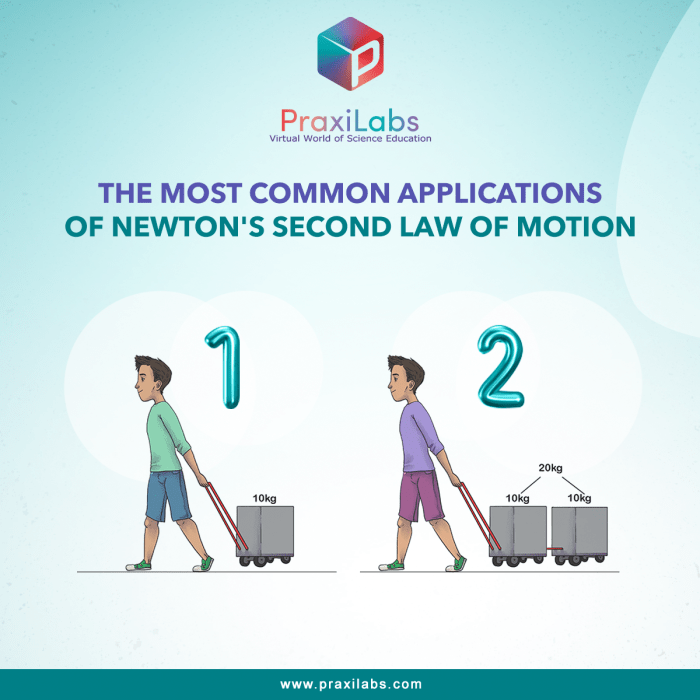
Newton’s laws of motion are fundamental principles in physics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting upon it. They form the basis for understanding a wide range of physical phenomena, from the motion of planets to the movement of everyday objects.
These laws revolutionized our understanding of the universe and laid the foundation for classical mechanics.
Historical Context and Impact, What is the 2nd law of motion
Sir Isaac Newton, an English physicist and mathematician, formulated these laws in the late 17th century. His work, published in the groundbreaking book *Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica* (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), revolutionized scientific thought.
Prior to Newton’s work, the understanding of motion was largely based on the ideas of Aristotle, who believed that a force was required to keep an object in motion. Newton’s laws challenged this notion and established a new framework for understanding motion.
Newton’s laws had a profound impact on scientific thought, providing a mathematical framework for understanding the physical world. They paved the way for advancements in fields such as astronomy, engineering, and technology.
For example, Newton’s laws of motion enabled scientists to calculate the orbits of planets and predict the motion of celestial bodies. This led to the development of modern astronomy and our understanding of the solar system.
Furthermore, Newton’s laws are essential for understanding the behavior of machines and structures, enabling engineers to design and build bridges, buildings, and vehicles.
Closing Notes: What Is The 2nd Law Of Motion
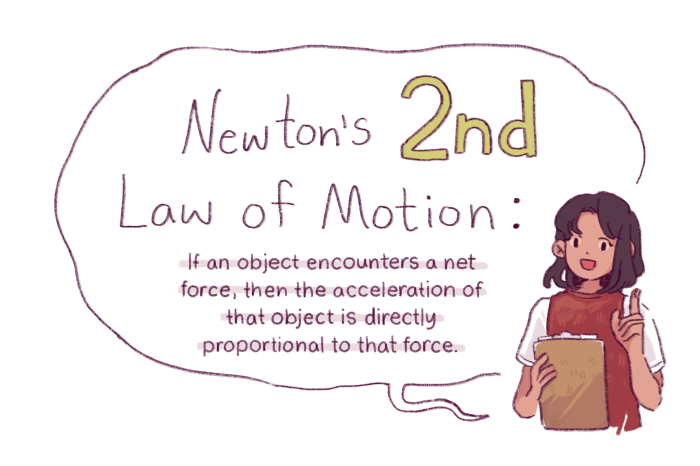
Newton’s Second Law of Motion is a powerful tool that allows us to predict and explain the motion of objects in various situations. From designing airplanes to understanding the movement of planets, this law plays a crucial role in our understanding of the physical world. By applying the principles of force, mass, and acceleration, we can analyze and predict the motion of objects in countless scenarios, making it an indispensable concept in fields ranging from engineering to sports.
Top FAQs
What is the difference between force and acceleration?
Force is a push or pull that can change an object’s motion. Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes. In simple terms, force causes acceleration.
Can an object have a constant velocity and still be accelerating?
No. Acceleration refers to a change in velocity. If an object’s velocity is constant, its acceleration is zero.
How does the Second Law of Motion apply to everyday objects?
It applies to everything! From driving a car to throwing a ball, the Second Law governs how objects respond to forces. The harder you push on the gas pedal, the faster the car accelerates. The more force you apply to a ball, the farther it travels.