
What is the hess law – What is Hess’s Law? Hess’s Law is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics that helps us understand and predict enthalpy changes in chemical reactions. It states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the pathway taken, meaning the overall energy change remains the same whether the reaction occurs in one step or multiple steps. This concept has wide-ranging applications in chemistry, allowing us to calculate enthalpy changes for reactions that are difficult or impossible to measure directly.
Imagine you are climbing a mountain. You can choose to take a steep, direct route or a more gradual, winding path. Regardless of the route you choose, the overall elevation change from the base to the summit remains the same. Similarly, in chemical reactions, Hess’s Law states that the overall enthalpy change remains constant even if the reaction proceeds through different steps or intermediates.
Introduction to Hess’s Law

Hess’s Law is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics that simplifies the calculation of enthalpy changes for chemical reactions. It states that the enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the path taken and depends only on the initial and final states of the reaction.
Hess’s Law is based on the concept of enthalpy, which is a thermodynamic property that represents the total heat content of a system. Enthalpy changes (ΔH) occur during chemical reactions, indicating whether heat is released (exothermic reaction, ΔH < 0) or absorbed (endothermic reaction, ΔH > 0).
Definition of Hess’s Law
Hess’s Law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is the same whether the reaction occurs in one step or in a series of steps. This implies that the overall enthalpy change of a reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes of the individual steps.
The enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway taken and depends only on the initial and final states of the reaction.
Real-World Example of Hess’s Law
One real-world example of Hess’s Law is the combustion of methane (CH4) to form carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). This reaction can be represented by the following equation:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
The enthalpy change for this reaction can be determined experimentally, but it can also be calculated using Hess’s Law. The combustion of methane can be broken down into two steps:
1. The combustion of methane to form carbon monoxide (CO) and water:
CH4(g) + 1.5O2(g) → CO(g) + 2H2O(l)
2. The oxidation of carbon monoxide to form carbon dioxide:
CO(g) + 0.5O2(g) → CO2(g)
The enthalpy changes for these two steps can be measured experimentally. According to Hess’s Law, the enthalpy change for the overall reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.
Therefore, the enthalpy change for the combustion of methane can be calculated as follows:
ΔHoverall = ΔHstep 1 + ΔHstep 2
This example demonstrates how Hess’s Law can be used to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by breaking it down into simpler steps.
Applications of Hess’s Law
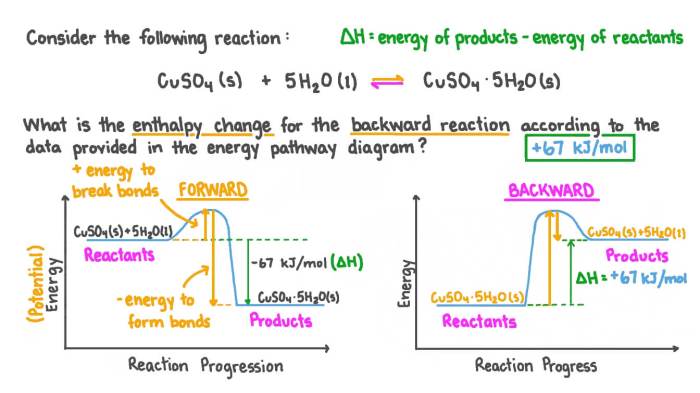
Hess’s Law is a fundamental principle in thermochemistry that has a wide range of applications in chemistry. It allows us to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction without directly measuring it in the laboratory. This is particularly useful for reactions that are difficult or impossible to carry out experimentally.
Applications of Hess’s Law in Chemistry
Hess’s Law is widely used in various fields of chemistry, including:
- Determining Enthalpy Changes of Reactions: Hess’s Law is the primary tool for calculating the enthalpy change of a reaction. It allows us to determine the enthalpy change of a reaction by combining the enthalpy changes of known reactions. For example, we can calculate the enthalpy change of the combustion of methane by combining the enthalpy changes of the combustion of carbon and hydrogen.
- Predicting the Feasibility of Reactions: Hess’s Law can help predict whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic. This information is crucial for understanding the spontaneity of a reaction and designing chemical processes.
- Calculating Bond Energies: Hess’s Law can be used to determine the bond energies of molecules. By combining the enthalpy changes of reactions involving the formation and breaking of bonds, we can calculate the energy required to break a specific bond.
- Studying Reaction Mechanisms: Hess’s Law can provide insights into the mechanism of a reaction. By comparing the enthalpy changes of different reaction pathways, we can identify the most likely mechanism.
Hypothetical Experiment to Determine Enthalpy Change
Let’s consider a hypothetical experiment to determine the enthalpy change of the following reaction:
C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g)
This reaction represents the formation of methane from its elements. We can use Hess’s Law to calculate the enthalpy change of this reaction by combining the enthalpy changes of the following known reactions:
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔH1 = -393.5 kJ/mol
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) ΔH2 = -571.6 kJ/mol
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ΔH3 = -890.4 kJ/mol
To determine the enthalpy change of the target reaction, we need to manipulate these known reactions to obtain the desired reactants and products. The first reaction needs to be reversed, the second reaction remains the same, and the third reaction also needs to be reversed. After manipulating the reactions, we need to add them together, ensuring that the coefficients of the reactants and products match those of the target reaction.
The enthalpy change of the target reaction can then be calculated by adding the enthalpy changes of the manipulated reactions:
ΔHreaction = -ΔH1 + ΔH2 – ΔH3 = 393.5 kJ/mol – 571.6 kJ/mol + 890.4 kJ/mol = -74.7 kJ/mol
This experiment demonstrates how Hess’s Law allows us to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by combining the enthalpy changes of known reactions.
Types of Reactions Where Hess’s Law is Applicable, What is the hess law
Hess’s Law is applicable to a wide variety of chemical reactions, including:
| Type of Reaction | Example |
|---|---|
| Combustion Reactions | CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) |
| Formation Reactions | C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g) |
| Neutralization Reactions | HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) |
| Decomposition Reactions | 2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g) |
| Phase Changes | H2O(l) → H2O(g) |
Closing Notes
Hess’s Law provides a powerful tool for understanding and predicting enthalpy changes in chemical reactions. It allows us to calculate enthalpy changes for complex reactions by breaking them down into simpler steps, making it a valuable tool in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and environmental science. By understanding Hess’s Law, we gain insights into the energy changes associated with chemical reactions, enabling us to predict reaction outcomes and design efficient processes.
FAQ Overview: What Is The Hess Law
How does Hess’s Law relate to the concept of state functions?
Hess’s Law is based on the concept of state functions. A state function is a property that depends only on the initial and final states of a system, not on the path taken to reach those states. Enthalpy is a state function, meaning the enthalpy change for a reaction depends only on the initial and final states of the reactants and products, not on the intermediate steps involved.
Can Hess’s Law be applied to reactions that involve multiple steps?
Yes, Hess’s Law is particularly useful for reactions that occur in multiple steps. By combining the enthalpy changes for each individual step, we can determine the overall enthalpy change for the entire reaction.
What are some limitations of Hess’s Law?
While Hess’s Law is a powerful tool, it has limitations. It applies only to reactions at constant pressure and temperature. Additionally, it may not be accurate for reactions that involve significant changes in volume or where the enthalpy changes for individual steps are not well-known.




