
What is the law of gravity? It’s a question that has intrigued philosophers and scientists for centuries, and it’s a force that shapes everything we see in the universe. From the apple falling from a tree to the planets orbiting the sun, gravity is the invisible force that holds everything together. It’s a fundamental force that governs the motion of objects and the structure of the cosmos.
Gravity is a force of attraction between any two objects with mass. The more massive the objects, the stronger the gravitational force between them. The closer the objects are, the stronger the gravitational force. This simple concept has profound implications, shaping the evolution of stars, galaxies, and even the very fabric of spacetime.
Introduction to Gravity
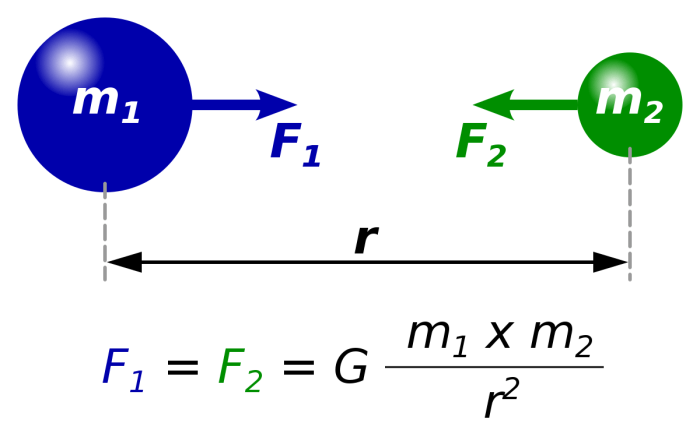
Gravity is a fundamental force of nature that governs the interactions between objects with mass. It is responsible for holding us to the Earth, keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun, and shaping the structure of the universe.
Gravity is an invisible force that pulls objects towards each other. The more massive an object is, the stronger its gravitational pull. This means that the Earth, with its massive size, exerts a strong gravitational force on us, keeping us firmly on its surface.
Examples of Gravity in Everyday Life
Gravity is a force we experience every day, often without even thinking about it. Here are some examples:
- When you jump, you eventually fall back down to the ground because of gravity.
- A ball thrown into the air will eventually come back down due to gravity.
- Water flows downhill due to gravity.
- The tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on the Earth’s oceans.
Historical Significance of Understanding Gravity
Understanding gravity has been crucial for the development of our understanding of the universe.
- Ancient Greeks: Early philosophers like Aristotle believed that objects fell to the ground because they were seeking their natural place. They had a rudimentary understanding of gravity.
- Isaac Newton: In the 17th century, Sir Isaac Newton revolutionized our understanding of gravity. He formulated the law of universal gravitation, which states that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This law explained why objects fall to the Earth, why the planets orbit the Sun, and why the Moon orbits the Earth.
- Albert Einstein: In the early 20th century, Albert Einstein developed the theory of general relativity, which provided a more complete understanding of gravity. He proposed that gravity is not a force, but rather a curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. This theory has had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe and has led to many important discoveries, including the existence of black holes.
Effects of Gravity
Gravity is a fundamental force that governs the motion of objects in the universe. It’s responsible for everything from the way an apple falls to the ground to the formation of galaxies. Let’s explore how gravity impacts objects near Earth’s surface and beyond.
Acceleration Due to Gravity, What is the law of gravity
Gravity exerts a constant force on objects near Earth’s surface, causing them to accelerate towards the ground. This acceleration is known as the acceleration due to gravity, denoted by ‘g’. The value of ‘g’ is approximately 9.8 m/s², meaning that an object’s velocity increases by 9.8 meters per second every second it falls.
Gravity’s Influence on Tides
The Moon’s gravitational pull plays a significant role in Earth’s tides. The Moon’s gravity pulls the water on the side of Earth closest to it, creating a bulge. A corresponding bulge occurs on the opposite side of Earth due to inertia. These bulges are the high tides, while the areas between the bulges experience low tides.
Gravity and Planetary Orbits
Gravity is the force that keeps planets in orbit around the Sun. The Sun’s massive gravitational pull attracts the planets, preventing them from flying off into space. The planets’ orbital paths are not perfectly circular but slightly elliptical, meaning they are not perfectly round. The elliptical shape arises from the interplay of gravity and the planets’ initial velocity.
Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity
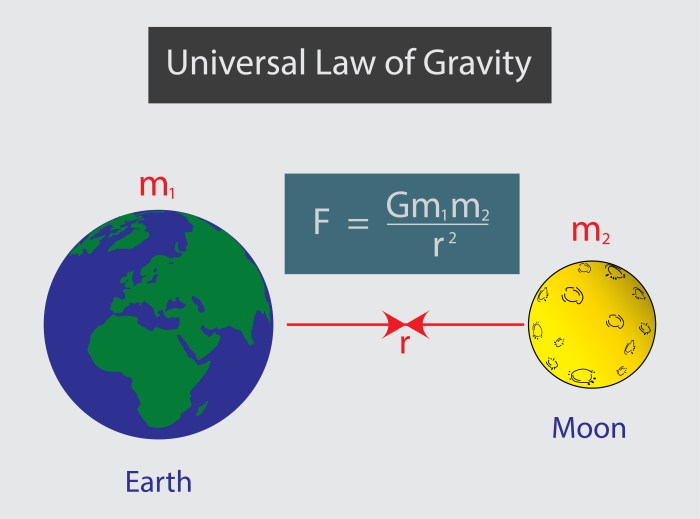
Einstein’s theory of general relativity, published in 1915, revolutionized our understanding of gravity. It proposed a fundamentally different view of gravity compared to Newton’s law of universal gravitation. While Newton’s law describes gravity as a force acting between objects with mass, Einstein’s theory explains gravity as a consequence of the curvature of spacetime.
Differences Between Newton’s Law and General Relativity
Einstein’s theory of general relativity differs from Newton’s law of universal gravitation in several key aspects:
- Nature of Gravity: Newton’s law describes gravity as a force acting between objects with mass, while general relativity explains gravity as a consequence of the curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy.
- Space and Time: Newton’s law treats space and time as separate and absolute entities, while general relativity views them as intertwined and dynamic, forming a four-dimensional spacetime continuum.
- Speed of Gravity: Newton’s law assumes gravity acts instantaneously, while general relativity predicts that gravitational interactions propagate at the speed of light.
- Strong Gravitational Fields: Newton’s law breaks down in extremely strong gravitational fields, such as those found near black holes, while general relativity provides a more accurate description of gravity in these extreme conditions.
Gravity as a Consequence of Spacetime Curvature
Einstein’s theory proposes that mass and energy warp the fabric of spacetime, creating a curvature. This curvature is what we perceive as gravity. Imagine a stretched sheet representing spacetime. Placing a heavy object on the sheet creates a dip or a curve. This curvature affects the path of objects moving near the heavy object, causing them to fall towards it. Similarly, the presence of massive objects like planets and stars warps spacetime, causing objects to fall towards them, thus explaining the force of gravity.
Phenomena Explained by General Relativity
General relativity explains various phenomena that cannot be accounted for by Newton’s law, including:
- Gravitational Lensing: Massive objects like galaxies and clusters of galaxies can bend light passing by them, creating multiple images of distant objects. This phenomenon, known as gravitational lensing, has been observed and provides strong evidence for the curvature of spacetime.
- Time Dilation: Time passes slower in stronger gravitational fields. This phenomenon, known as time dilation, has been verified by experiments involving atomic clocks placed at different altitudes. For instance, GPS satellites, orbiting in a weaker gravitational field, experience time slightly faster than clocks on Earth, and this difference must be accounted for to ensure accurate positioning.
- Black Holes: General relativity predicts the existence of black holes, regions of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Black holes have been observed indirectly through their gravitational effects on surrounding matter and the emission of X-rays.
- Gravitational Waves: General relativity predicts the existence of gravitational waves, ripples in the fabric of spacetime caused by accelerating massive objects. These waves were first detected in 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), providing further confirmation of Einstein’s theory.
Final Thoughts: What Is The Law Of Gravity
Understanding the law of gravity is a journey into the heart of the universe. It’s a force that is both familiar and mysterious, holding the key to unlocking the secrets of our cosmos. From the simple act of walking to the vast expanse of space, gravity is a constant presence, shaping our world in countless ways.
FAQ Compilation
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force of gravity acting on that object. So, an object’s mass stays the same regardless of where it is, but its weight can change depending on the gravitational field it’s in.
Why does the Earth have gravity?
Earth has gravity because it has mass. The more mass an object has, the stronger its gravitational pull. Earth’s large mass creates a strong gravitational field that pulls everything towards its center.
What is the acceleration due to gravity?
The acceleration due to gravity is the rate at which an object accelerates towards the Earth due to gravity. It’s approximately 9.8 m/s² at the Earth’s surface.
What is the relationship between gravity and time?
Einstein’s theory of general relativity tells us that gravity can warp spacetime, which means that time can actually slow down near massive objects. This effect is known as gravitational time dilation.




