
What states have common law marriage? This question delves into a fascinating aspect of American law, where couples can be legally recognized as married without a formal ceremony. While not recognized in all states, common law marriage offers a unique path to legal union, rooted in history and evolving legal interpretations.
Understanding the states that recognize common law marriage, the requirements for establishing such a union, and its legal implications is crucial for individuals considering this path. Whether you’re curious about the history of common law marriage, the legal complexities, or the practical considerations, this guide provides valuable insights.
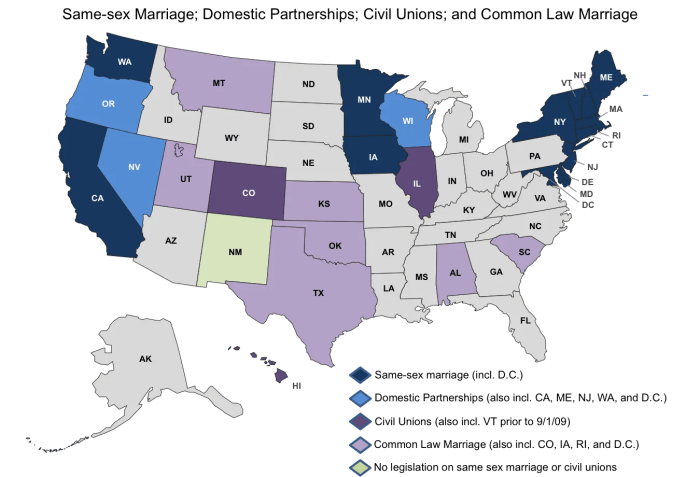
Termination of Common Law Marriage: What States Have Common Law Marriage

Ending a common law marriage can be complex and requires understanding the specific laws of the state where the relationship was established. This section will Artikel the methods for ending a common law marriage and discuss potential legal issues that may arise.
Methods for Ending a Common Law Marriage
Common law marriages can be terminated in various ways, including:
- Mutual Agreement: Both parties can mutually agree to end the relationship, often formalized in writing to avoid future disputes. This can be as simple as a written agreement or a more formal separation agreement.
- Separation: In some states, a physical separation with the intent to end the marriage can terminate the relationship. The specific requirements for separation vary by state, including the duration of the separation and the intent to end the relationship.
- Death of a Spouse: The death of one spouse automatically ends the common law marriage.
- Court Order: Similar to traditional marriages, a court order can dissolve a common law marriage. This usually involves a legal process with specific requirements for filing and serving legal documents.
Formal Dissolution of a Common Law Marriage
Formal dissolution of a common law marriage typically involves a legal process similar to a divorce. This process often includes:
- Filing a Petition: One party files a petition for dissolution of the common law marriage, outlining the reasons for the termination.
- Service of Process: The petition is served on the other party, officially notifying them of the legal proceedings.
- Discovery: Both parties exchange information and evidence relevant to the case, such as financial records, property ownership, and details about the relationship.
- Mediation or Trial: Parties may attempt to reach a settlement through mediation or go to trial if they cannot agree on the terms of the dissolution.
- Court Order: If the case proceeds to trial, the court issues an order formally dissolving the common law marriage. This order typically addresses issues like property division, spousal support, and child custody (if applicable).
Potential Legal Issues During Termination, What states have common law marriage
The termination of a common law marriage can raise various legal issues, including:
- Property Division: States have different laws regarding the division of property acquired during a common law marriage. It’s crucial to understand the specific laws of the state where the relationship existed to ensure a fair distribution of assets.
- Spousal Support: Depending on the state, one party may be entitled to spousal support (alimony) after the termination of the common law marriage. Factors like the duration of the relationship, earning capacity, and financial contributions are considered.
- Child Custody and Support: If children were born during the common law marriage, custody and support arrangements must be established. These issues are typically addressed in the dissolution order or through separate legal proceedings.
- Debts: Debts incurred during the common law marriage may need to be addressed. Courts often consider the nature of the debt and the parties’ financial contributions to determine liability.
- Legal Recognition: One of the biggest issues is establishing the existence of the common law marriage. States have strict requirements, and proving the existence of the relationship can be challenging.
Legal Advice and Considerations
It is crucial to consult with an attorney before entering into a common law marriage. Seeking legal advice can help you understand the legal implications of this commitment and ensure that your rights and interests are protected.
Potential Legal Issues
Understanding the potential legal issues associated with common law marriage is essential for informed decision-making. Common law marriage can lead to legal complexities, particularly in situations involving property division, child custody, and spousal support.
- Property Division: In a common law marriage, property acquired during the relationship is typically considered marital property, subject to division upon separation or divorce. Determining the ownership and division of assets can be complex and may require legal intervention.
- Child Custody and Support: If children are born or adopted during a common law marriage, legal issues related to child custody and support may arise upon separation. The legal framework for child custody and support can vary depending on the state’s laws.
- Spousal Support: In some states, one spouse may be entitled to spousal support (alimony) from the other spouse following separation or divorce. The eligibility and amount of spousal support can be determined by factors such as the length of the relationship, the financial contributions of each spouse, and the earning capacity of each spouse.
- Debt and Liability: Common law spouses may be held jointly liable for debts incurred during the relationship. This can include financial obligations such as credit card debt, loans, and mortgages.
Potential Risks
Common law marriage presents potential risks that individuals should carefully consider before entering into such a relationship.
- Lack of Legal Recognition in Some States: Common law marriage is not recognized in all states. Individuals planning to enter into a common law marriage should ensure that it is legal in their state of residence.
- Difficulty Proving the Relationship: Establishing the existence of a common law marriage can be challenging, requiring clear and convincing evidence that the couple intended to be married. This evidence may include shared finances, joint ownership of property, and public declarations of marriage.
- Unintended Consequences: Common law marriage can have unintended consequences, such as the potential for unexpected legal obligations and financial burdens. Individuals should carefully consider the potential implications before entering into such a relationship.
- Lack of Formal Legal Protections: Common law marriage does not provide the same legal protections as a formal marriage, such as the right to inherit property or receive benefits under a spouse’s life insurance policy.
Ending Remarks

The concept of common law marriage presents a compelling blend of tradition and legal evolution. While not universally recognized, it offers a path to legal recognition for couples who choose to forgo a formal ceremony. Understanding the requirements, legal implications, and potential risks associated with common law marriage is crucial for individuals considering this option. Seeking legal advice before entering into a common law marriage ensures clarity, protection, and a smooth path for the future.
FAQ Corner
How do I end a common law marriage?
Ending a common law marriage usually involves a formal dissolution process similar to a divorce. Specific procedures vary by state. Consult with a lawyer to ensure proper legal steps are taken.
What are the benefits of common law marriage?
Benefits include legal recognition of the relationship, inheritance rights, and access to spousal benefits such as health insurance.
What are the risks of common law marriage?
Risks include potential legal disputes regarding the relationship’s validity, challenges in proving intent to be married, and complications during termination.




