When did car seat laws start sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Car seat laws, designed to protect our most vulnerable passengers, have a fascinating history that reflects the evolving understanding of child safety in vehicles. From the early days of rudimentary safety devices to the advanced technology of modern car seats, this journey unveils the tireless efforts of individuals and organizations dedicated to safeguarding children on the road.
The evolution of car seat laws is a testament to the progress made in child safety, driven by a combination of research, advocacy, and legislative action. This exploration delves into the key events and factors that shaped the development of these regulations, showcasing the remarkable impact they have had on reducing child injuries and fatalities in motor vehicle accidents.
History of Car Seat Laws

The history of car seat laws in the United States reflects a gradual but significant evolution in understanding the importance of child safety in vehicles. Early efforts focused on promoting the use of car seats, but as research highlighted the effectiveness of these devices, regulations became more stringent, mandating their use and establishing specific safety standards.
Early Car Seat Laws and Their Impact
Early car seat laws were largely focused on promoting the use of car seats rather than mandating them. These early efforts laid the foundation for the development of more comprehensive and effective regulations.
- 1960s: The first car seat was introduced, and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) was established.
- 1971: The first federal safety standards for car seats were established, but these standards were not mandatory.
- 1978: The first mandatory car seat law was passed in the state of Massachusetts.
- 1980s: Several other states followed suit, and the NHTSA began promoting the use of car seats through public awareness campaigns.
These early car seat laws had a significant impact on child safety. Studies showed that the use of car seats significantly reduced the risk of death and serious injury in car accidents. This led to a growing demand for more comprehensive car seat regulations.
Federal Regulations and Mandates: When Did Car Seat Laws Start
The safety of children in vehicles has been a major concern for decades, leading to the development and implementation of federal regulations aimed at ensuring the proper use of car seats. These regulations have significantly impacted the design, manufacturing, and usage of car seats, ultimately contributing to a substantial reduction in child passenger fatalities.
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) 213
This standard, established by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), Artikels the requirements for child restraint systems, including car seats, booster seats, and other devices designed to protect children in motor vehicles. FMVSS 213 covers a wide range of aspects, including:
- Performance Requirements: The standard specifies the minimum performance requirements for car seats, such as their ability to withstand crash forces and protect the child in various crash scenarios.
- Labeling and Instructions: Car seats must have clear and concise labeling that provides information about the seat’s proper use, weight and height limits, and other essential details.
- Testing Procedures: FMVSS 213 mandates specific testing procedures to ensure that car seats meet the safety standards. These tests simulate various crash conditions to evaluate the seat’s ability to protect the child.
- Retention Systems: The standard addresses the design and functionality of car seat harness systems, ensuring that they are secure and effective in restraining the child during a crash.
- Installation: FMVSS 213 includes provisions for the installation of car seats, specifying the appropriate methods for securing the seat in the vehicle and ensuring a proper fit.
Role of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
The NHTSA plays a pivotal role in ensuring car seat safety by:
- Developing and Enforcing FMVSS 213: The NHTSA is responsible for setting the safety standards for car seats and enforcing compliance among manufacturers.
- Conducting Research and Testing: The NHTSA conducts extensive research and testing to evaluate the effectiveness of car seats and identify areas for improvement.
- Public Education and Outreach: The NHTSA plays a crucial role in educating the public about car seat safety, providing information on proper installation, usage, and maintenance.
- Recalls and Investigations: In the event of safety concerns, the NHTSA has the authority to issue recalls for car seats that fail to meet safety standards or pose a risk to children.
Impact of Federal Regulations on Car Seat Design and Usage
The implementation of federal regulations has significantly influenced the design and usage of car seats:
- Improved Safety Features: Federal regulations have driven manufacturers to incorporate advanced safety features in car seats, such as side impact protection, energy-absorbing materials, and improved harness systems.
- Standardized Design and Labeling: The regulations have standardized the design and labeling of car seats, making it easier for consumers to understand and compare different models.
- Increased Awareness and Compliance: The public awareness campaigns and enforcement efforts by the NHTSA have significantly increased awareness about car seat safety, leading to greater compliance with regulations.
- Reduction in Child Passenger Fatalities: The implementation of car seat regulations has been instrumental in reducing child passenger fatalities, demonstrating the effectiveness of these measures in protecting children on the road.
Types of Car Seats
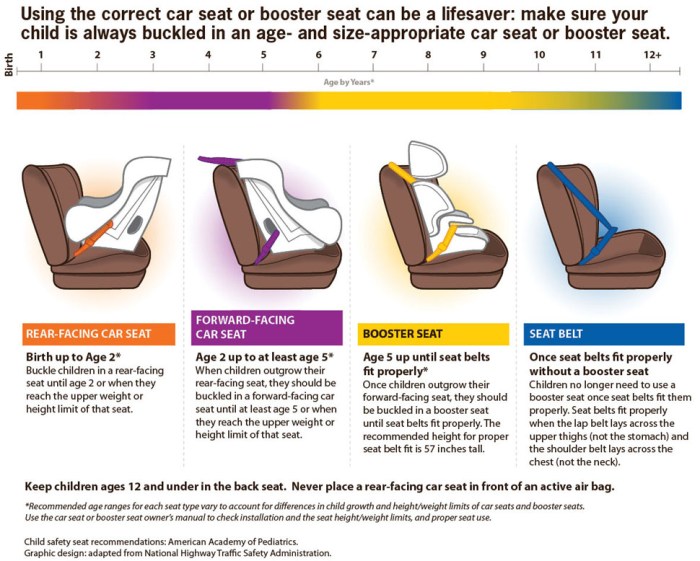
Car seats are essential safety devices for children, providing crucial protection in the event of a car accident. Choosing the right car seat for your child’s age, weight, and height is crucial for their safety. There are four main types of car seats: rear-facing, forward-facing, booster seats, and convertible seats. Each type is designed to provide optimal protection for children at different developmental stages.
Rear-Facing Car Seats
Rear-facing car seats are designed for infants and toddlers, providing the safest position for their delicate bodies. These seats are positioned facing the rear of the vehicle, ensuring that in the event of a collision, the force of impact is distributed across the child’s back and head, minimizing the risk of serious injury.
Rear-facing car seats are typically used for children from birth until they reach a certain weight or height limit, usually around 35 pounds or 40 pounds, depending on the specific car seat model. The recommended age for rear-facing is at least two years old.
“Keep your child rear-facing as long as possible, as this is the safest position for them.” – National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
Features of Rear-Facing Car Seats
- Harness System: Rear-facing car seats have a five-point harness system that secures the child in the seat. The harness straps are adjusted to fit snugly around the child’s shoulders, hips, and crotch, ensuring they are securely held in place.
- Recline Adjustment: These seats often have multiple recline positions to accommodate the child’s growing body. This helps to ensure a comfortable and safe position for the child.
- Base: Many rear-facing car seats have a base that can be installed in the vehicle. This provides a stable foundation for the seat and makes it easier to install and remove.
Forward-Facing Car Seats
Once a child reaches the weight and height requirements for their rear-facing car seat, they can transition to a forward-facing car seat. These seats are designed for children who are typically older and heavier than those using rear-facing seats.
Forward-facing car seats are generally used for children from around 20 pounds to 65 pounds or until they reach a specific height requirement. The specific weight and height limits vary depending on the car seat model.
Features of Forward-Facing Car Seats
- Harness System: Forward-facing car seats also have a five-point harness system to secure the child in the seat. However, the harness straps are adjusted differently to accommodate the child’s larger size.
- Top Tether: Forward-facing car seats have a top tether strap that attaches to an anchor point in the vehicle’s trunk. This strap helps to stabilize the seat and prevent it from rotating in a crash.
- LATCH System: Most forward-facing car seats use the LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) system for installation. This system provides a more secure and easier installation method compared to using the vehicle’s seat belt.
Booster Seats
When a child outgrows their forward-facing car seat, they can transition to a booster seat. Booster seats are designed to elevate the child so that the vehicle’s seat belt fits them properly. The seat belt should fit snugly across the child’s shoulders and hips, not their stomach or neck.
Booster seats are typically used for children between 40 and 100 pounds or until they reach a specific height requirement, usually around 4’9″. The specific weight and height limits vary depending on the booster seat model.
Features of Booster Seats
- Backrest: Some booster seats have a backrest, which provides additional support for the child’s head and neck.
- Armrests: Booster seats with armrests can provide added comfort and support for the child.
- Cupholders: Some booster seats have cupholders, which can be convenient for the child to hold drinks or snacks.
Convertible Car Seats
Convertible car seats are a versatile option that can be used in both rear-facing and forward-facing positions. This type of car seat is ideal for families who want to use one seat for their child for a longer period.
Convertible car seats typically have a weight and height range for rear-facing and forward-facing positions, allowing them to accommodate a wider range of child sizes.
Features of Convertible Car Seats
- Rear-Facing and Forward-Facing Positions: Convertible car seats can be adjusted to face either the rear or the front of the vehicle, making them suitable for use from infancy to toddlerhood.
- Adjustable Harness: The harness system on convertible car seats can be adjusted to accommodate the child’s growing size.
- LATCH and Seat Belt Installation: Convertible car seats can be installed using either the LATCH system or the vehicle’s seat belt, providing flexibility for installation in different vehicles.
Importance of Proper Installation
Proper car seat installation is crucial for ensuring your child’s safety in the event of a car accident. A car seat that is not installed correctly can move around in a crash, increasing the risk of serious injury or even death.
The good news is that installing a car seat correctly is not as difficult as it may seem. There are many resources available to help parents and caregivers learn how to do it right. By following the instructions carefully and taking the time to do it properly, you can help keep your child safe.
Types of Car Seat Installation
The specific steps for installing a car seat will vary depending on the type of car seat and the vehicle. However, there are some general guidelines that apply to all car seat installations.
- Rear-Facing Car Seats: Rear-facing car seats are designed for infants and toddlers up to a certain weight and height. These seats should be installed in the back seat, facing the rear of the vehicle. Rear-facing car seats are the safest option for infants and toddlers, as they provide the best protection for their head, neck, and spine in the event of a crash.
- Forward-Facing Car Seats: Forward-facing car seats are designed for older toddlers and children who have outgrown their rear-facing car seats. These seats should be installed in the back seat, facing the front of the vehicle. When installing a forward-facing car seat, it’s important to make sure the harness is tight and the seat is secured properly.
- Booster Seats: Booster seats are designed for children who have outgrown their forward-facing car seats. These seats should be installed in the back seat, and the child should be wearing a lap and shoulder belt. Booster seats help position the lap and shoulder belt correctly to provide optimal protection in the event of a crash.
Steps for Installing a Car Seat
The specific steps for installing a car seat will vary depending on the type of car seat and the vehicle. However, here are some general guidelines to follow:
- Read the car seat manual: Before installing a car seat, it’s important to read the manual carefully. The manual will provide specific instructions for installing the car seat in your vehicle.
- Choose the right seat: The car seat should be installed in the back seat of the vehicle, in the middle position if possible. This is the safest location for a car seat, as it is furthest away from the impact point in a crash.
- Install the car seat: Install the car seat according to the instructions in the manual. Make sure the seat is securely fastened and that the harness is tight.
- Check for movement: Once the car seat is installed, check to make sure it doesn’t move more than an inch in any direction. If the car seat moves more than an inch, it is not installed correctly.
- Adjust the harness: The harness should be tight enough that you can’t pinch any excess webbing between your fingers.
- Secure the car seat: Secure the car seat using the vehicle’s seat belt or LATCH system, depending on the car seat model and vehicle.
Troubleshooting Common Car Seat Installation Problems
Here are some common car seat installation problems and tips for troubleshooting them:
- The car seat is too loose: If the car seat is too loose, it may not be installed correctly. Check the manual for the correct installation instructions. Make sure the car seat is securely fastened to the vehicle’s seat belt or LATCH system.
- The car seat is too tight: If the car seat is too tight, it may be difficult to install or remove. Check the manual for the correct installation instructions. Make sure the car seat is not being squeezed or pinched.
- The car seat is not level: If the car seat is not level, it may not be installed correctly. The car seat should be level from side to side and front to back. You can use a level to check.
- The harness is too loose: If the harness is too loose, it may not be able to properly restrain your child in the event of a crash. Make sure the harness is tight enough that you can’t pinch any excess webbing between your fingers.
- The car seat is not compatible with the vehicle: Some car seats are not compatible with all vehicles. Check the car seat manual to make sure it is compatible with your vehicle.
Car Seat Safety Tips
Ensuring your child’s safety in a car is paramount, and using a car seat correctly is a crucial part of that. This section provides essential safety tips to help you maximize the protection your car seat offers.
Choosing the Right Car Seat
Selecting the right car seat for your child’s age, weight, and height is crucial. Car seats are categorized based on these factors:
- Rear-facing car seats: These are designed for infants and toddlers up to a certain weight or height, typically 20-40 pounds and 1 year old. They are generally considered the safest option for infants, as they provide optimal head and neck support in case of a crash.
- Forward-facing car seats: These are for older toddlers and preschoolers who have outgrown their rear-facing car seats. They typically accommodate children weighing 20-65 pounds and are generally used until the child reaches the maximum height and weight limits of the seat.
- Booster seats: Booster seats are for older children who have outgrown forward-facing car seats but are still too small to use adult seat belts safely. They raise the child’s height, ensuring the adult seat belt fits properly across their chest and lap.
Proper Harness Adjustment, When did car seat laws start
The harness should be snug and fit correctly to provide maximum protection in case of a crash.
- Shoulder straps: The shoulder straps should be at or above your child’s shoulders. They should not be too loose or too tight.
- Chest clip: The chest clip should be at your child’s armpit level.
- Harness straps: The harness straps should be snug enough that you can only fit one or two fingers between the strap and your child’s chest.
Seat Position
The position of the car seat within the vehicle is critical.
- Rear-facing seats: Rear-facing car seats should be installed in the back seat, preferably in the middle position. This position offers the most protection in case of a crash.
- Forward-facing seats: Forward-facing car seats should also be installed in the back seat, ideally in the middle position. If this is not possible, the side seat is the next safest option.
- Booster seats: Booster seats should be installed in the back seat, with the child sitting in the seat with the adult seat belt properly fastened.
Common Car Seat Safety Mistakes to Avoid
- Not installing the car seat correctly: This is one of the most common mistakes. Car seats should be installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions and the vehicle’s owner’s manual.
- Using the wrong type of car seat: It is important to choose the right car seat for your child’s age, weight, and height.
- Not keeping your child in a car seat for long enough: Children should remain in a car seat until they meet the maximum height and weight limits of the seat.
- Leaving your child unattended in a car seat: Never leave your child unattended in a car seat, even for a short time.
Car Seat Recalls and Updates
Car seat recalls are issued when a manufacturer discovers a safety defect in a car seat that could potentially harm a child. These recalls are crucial for ensuring the safety of children while traveling in vehicles. It is essential to stay informed about car seat recalls and updates to ensure your child’s safety.
Checking for Car Seat Recalls
Staying informed about car seat recalls is essential. There are several ways to check for recalls:
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA): The NHTSA is the primary source for information about car seat recalls. You can check for recalls by entering your car seat’s model number or VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) on the NHTSA website.
- Manufacturer’s Website: Most car seat manufacturers have a dedicated section on their website where they list any active recalls. You can also sign up for email alerts to receive notifications about recalls for your specific car seat model.
- Car Seat Registry: Several organizations offer car seat registries, where you can register your car seat and receive notifications about recalls. These registries often provide additional information about car seat safety and updates.
Importance of Following Manufacturer Instructions and Using Updated Car Seats
It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing and using your car seat. Car seat manufacturers continually update their products and safety recommendations. Therefore, it is essential to stay informed about any updates or changes to your car seat’s instructions. Here are some key points to remember:
- Read the Manual: Always refer to the car seat’s instruction manual for the latest information on installation, usage, and weight and height limits.
- Check for Updates: Visit the manufacturer’s website regularly for any updates or changes to the car seat’s instructions or safety recommendations.
- Use Updated Seats: If your car seat is recalled, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for repair or replacement. Using an outdated or recalled car seat can compromise your child’s safety.
Impact of Car Seat Laws on Child Safety
Car seat laws have had a profound impact on child safety, significantly reducing the number of injuries and fatalities in motor vehicle accidents. These laws mandate the use of appropriate car seats for children based on their age, weight, and height, ensuring they are properly restrained and protected in the event of a crash.
Child Fatality Rates Before and After Car Seat Laws
Car seat laws have been instrumental in reducing child fatality rates in motor vehicle accidents. Before the widespread implementation of these laws, child fatalities were significantly higher. For example, in the United States, the fatality rate for children under the age of five in motor vehicle accidents was 2.5 per 100,000 in 1970. This rate has dramatically decreased since the implementation of car seat laws. By 2020, the fatality rate for this age group had fallen to 0.3 per 100,000, representing an 88% reduction.
Ending Remarks
As we conclude this exploration of car seat laws, it’s clear that the journey to ensure child safety in vehicles has been a long and impactful one. From the early days of basic car seat designs to the sophisticated technology of today, the evolution of car seat laws reflects a growing understanding of the importance of protecting our youngest passengers. By understanding the history, regulations, and best practices surrounding car seats, we can continue to advocate for safer roads and a brighter future for our children.
Clarifying Questions
What is the minimum age for a child to ride in a car without a car seat?
The minimum age for a child to ride in a car without a car seat varies by state, but it is generally recommended that children ride in a car seat until they reach the age of 8 or the height and weight requirements of the car seat manufacturer are met.
What is the difference between a convertible car seat and a booster seat?
A convertible car seat can be used rear-facing for infants and toddlers, and then transitioned to forward-facing as the child grows. A booster seat is designed for older children who have outgrown forward-facing car seats but are not yet tall enough to use the vehicle’s seat belt alone.
How often should I check for car seat recalls?
It is recommended to check for car seat recalls regularly, at least once a year. You can check for recalls on the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) website or on the manufacturer’s website.