- When Was Maritime Law Created?
- Maritime Law: The Ancient Roots
- The Modern Era of Maritime Law
- The Evolution of Maritime Law
- Table: Key Developments in Maritime Law
- Conclusion
-
FAQ about When Was Maritime Law Created
- When was maritime law created?
- Who created the first maritime law?
- When was the Rhodian Sea Law created?
- When was maritime law incorporated into Roman law?
- When was maritime law codified in the Middle Ages?
- When was the first modern maritime law code adopted?
- When was the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) adopted?
- When was the International Maritime Organization (IMO) established?
- When was the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea (ITLOS) established?
- When was the first maritime arbitration center established?
When Was Maritime Law Created?
Ahoy There, Readers!
Gather ’round, dear readers, and let’s embark on a voyage through the murky depths of maritime law. When was this intricate system of regulations born, you may ask? Well, buckle up as we dive into the annals of history to uncover the genesis of this nautical code.
Maritime Law: The Ancient Roots
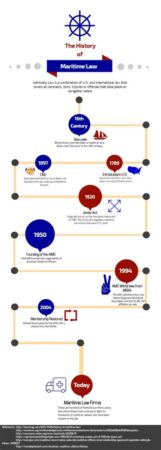
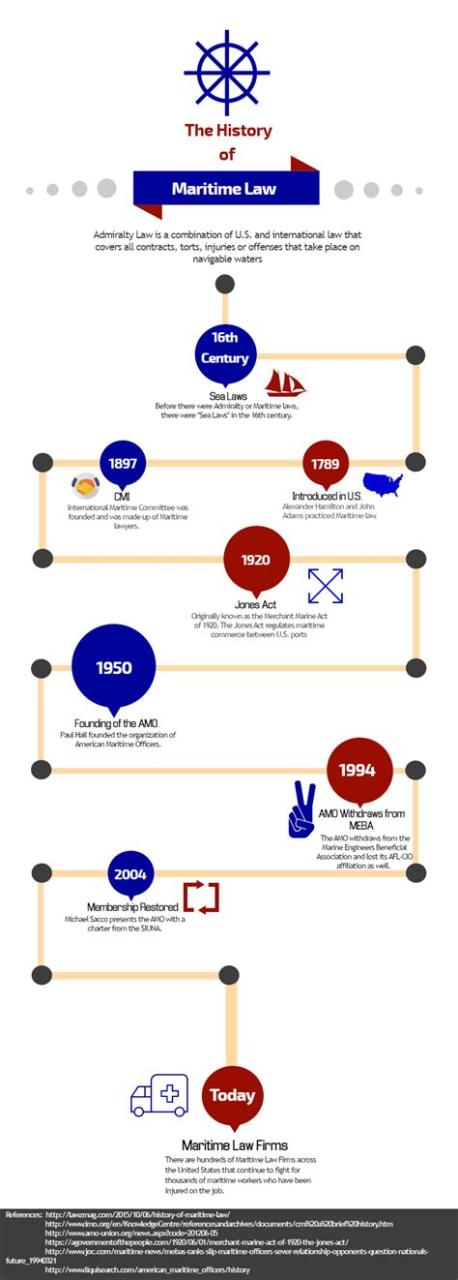
Maritime law, a body of rules governing the conduct of seafarers, can trace its origins back to the dawn of civilization. As early as 1750 B.C., the Code of Hammurabi contained provisions related to maritime trade and navigation. The ancient Greeks and Romans also established laws governing seafaring, evidenced by the Rhodian Sea Law and the Lex Rhodia respectively.
The Rise of Admiralty Courts
With the growth of maritime commerce during the Middle Ages, the need for specialized courts to adjudicate disputes arose. Admiralty courts emerged in England and other maritime nations to handle cases involving maritime contracts, piracy, and collisions at sea. These courts applied a distinct set of laws derived from ancient codes and customs known as the law of the sea.
The Modern Era of Maritime Law
The 16th and 17th centuries witnessed significant developments in maritime law. The Spanish Empire codified maritime laws in the Laws of the Indies, while the French developed the Ordonnance de la Marine. These codes influenced the development of modern maritime law in Europe and beyond.
International Conventions and Treaties
In the 19th and 20th centuries, international conventions and treaties played a crucial role in shaping maritime law. The Hague Conference on Private International Law (1894) produced a series of conventions on topics such as collisions and salvage. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (1982) codified a comprehensive framework for all aspects of ocean use.
The Evolution of Maritime Law
Throughout history, maritime law has continuously evolved to meet the changing needs of seafaring and global commerce. Technological advancements, emerging industries, and environmental concerns have all contributed to the expansion and refinement of this body of law.
Recent Developments
In recent years, maritime law has addressed issues such as maritime cyber security, the regulation of offshore energy development, and the protection of marine ecosystems. As new technologies and challenges arise, maritime law will continue to adapt to ensure the safety, fairness, and sustainability of maritime activities.
Table: Key Developments in Maritime Law
| Period | Event |
|---|---|
| 1750 B.C. | Code of Hammurabi includes provisions on maritime trade |
| 6th Century B.C. | Rhodian Sea Law establishes rules for maritime commerce and navigation |
| 13th Century A.D. | Admiralty courts emerge in England and other maritime nations |
| 16th Century A.D. | Spanish Laws of the Indies and French Ordonnance de la Marine codify maritime laws |
| 19th Century A.D. | Hague Conference produces conventions on collisions and salvage |
| 1982 A.D. | United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea codifies a comprehensive framework for ocean use |
| 21st Century A.D. | Maritime law addresses maritime cyber security, offshore energy development, and marine ecosystem protection |
Conclusion
So, dear readers, the origins of maritime law can be traced back to ancient times, when civilizations recognized the need to regulate seafaring and trade. Through the ages, various codes, conventions, and courts have shaped the evolution of maritime law, which continues to adapt to the ever-changing challenges of the maritime industry.
If you’re curious about other fascinating topics, be sure to check out our other articles! We promise to take you on captivating journeys through the world of knowledge.
FAQ about When Was Maritime Law Created
When was maritime law created?
Answer: The origins of maritime law can be traced back to ancient times, with the earliest known maritime codes dating back to the Babylonians in the 18th century BC.
Who created the first maritime law?
Answer: The first maritime law is attributed to the Rhodians, a seafaring people who lived on the island of Rhodes in the Aegean Sea. They developed a comprehensive set of maritime regulations known as the Rhodian Sea Law, which influenced maritime law for centuries to come.
When was the Rhodian Sea Law created?
Answer: The Rhodian Sea Law was developed gradually over time, with the earliest known fragments dating back to the 7th century BC. It reached its peak around the 3rd century BC and remained influential until the rise of the Roman Empire.
When was maritime law incorporated into Roman law?
Answer: Maritime law was incorporated into Roman law during the reign of Emperor Augustus (27 BC – 14 AD). The Roman jurist Ulpian compiled a comprehensive treatise on maritime law, which became the basis for later maritime codes.
When was maritime law codified in the Middle Ages?
Answer: Maritime law was codified in a number of medieval maritime codes, including the Consolato del Mare (14th century), the Laws of Oléron (12th century), and the Hanseatic League Laws (14th century).
When was the first modern maritime law code adopted?
Answer: The first modern maritime law code was adopted by France in 1681. It was known as the Ordonnance de la Marine and served as a model for maritime law codes in other countries.
When was the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) adopted?
Answer: UNCLOS was adopted in 1982 and entered into force in 1994. It is the most comprehensive international agreement on maritime law, covering a wide range of issues including territorial waters, exclusive economic zones, and freedom of navigation.
When was the International Maritime Organization (IMO) established?
Answer: IMO was established in 1948 to promote maritime safety and security. It develops and maintains international standards and regulations for shipping.
When was the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea (ITLOS) established?
Answer: ITLOS was established in 1996 to resolve disputes relating to the interpretation or application of UNCLOS. It is the only international court dedicated to maritime law.
When was the first maritime arbitration center established?
Answer: The first maritime arbitration center was established in London in 1892 to provide a forum for the resolution of maritime disputes. Maritime arbitration centers have since been established in many other countries and play a vital role in the enforcement of maritime law.