
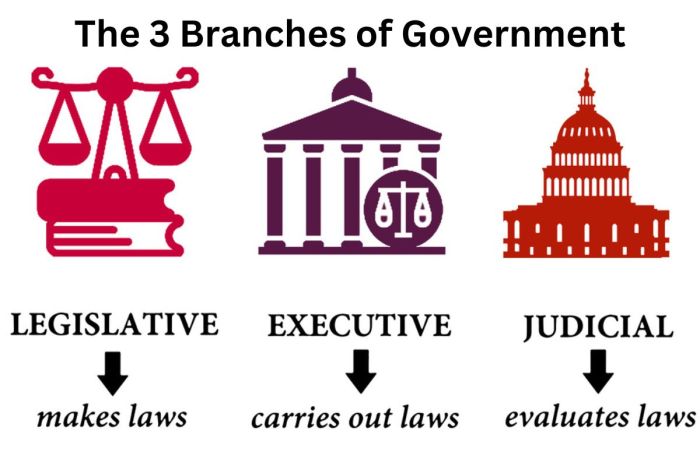
Which branch makes laws sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. In the United States, the legislative branch, composed of Congress, holds the primary responsibility for creating and enacting laws. This process, often described as a complex dance of checks and balances, involves intricate steps, from the introduction of a bill to its eventual signing into law.
This exploration delves into the heart of American democracy, showcasing the power dynamics between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches as they navigate the intricate process of lawmaking. We’ll examine the roles of Congress, the President, and the courts in shaping the laws that govern our nation, revealing the delicate balance that ensures a system of checks and balances.
The People and Lawmaking
The legislative process is not solely confined to the halls of government. Citizens play a vital role in shaping laws through various avenues of engagement. Public opinion, lobbying efforts, and advocacy groups all contribute to the dynamic interplay between the people and the lawmaking process.
Public Opinion’s Influence on Legislation, Which branch makes laws
Public opinion can exert significant influence on the legislative process, shaping the priorities of lawmakers and ultimately impacting the laws that are enacted. This influence can manifest in various ways:
- Electoral Pressure: Public opinion on key issues can influence the decisions of elected officials, who are ultimately accountable to their constituents. For example, a surge in public support for environmental protection could lead lawmakers to prioritize legislation addressing climate change.
- Public Protests and Demonstrations: Large-scale protests and demonstrations can raise awareness about specific issues and put pressure on lawmakers to address them. The civil rights movement, for instance, mobilized public opinion and led to significant legislative changes in the area of racial equality.
- Opinion Polls and Surveys: Opinion polls and surveys provide valuable insights into public sentiment on various issues, enabling lawmakers to gauge public support for proposed legislation. Lawmakers may use this data to tailor their legislative proposals to align with public opinion.
Lobbying and Advocacy Groups in Lawmaking
Lobbying and advocacy groups play a crucial role in shaping legislation by influencing lawmakers and public opinion. They represent various interests, from corporations to non-profit organizations, and use various strategies to advocate for their policy positions:
- Direct Lobbying: Lobbyists engage in direct communication with lawmakers, providing information and arguments in support of their policy positions. They may meet with legislators, attend hearings, and provide testimony to influence the legislative process.
- Grassroots Mobilization: Advocacy groups often engage in grassroots mobilization, encouraging their members and supporters to contact their elected officials and advocate for specific policies. This can involve phone calls, emails, and social media campaigns to amplify their message.
- Public Education and Awareness: Lobbying and advocacy groups often engage in public education campaigns to raise awareness about specific issues and build support for their policy positions. They may use media outlets, public events, and online platforms to disseminate their message.
Citizen Engagement in Lawmaking
Citizens can actively participate in the lawmaking process through various avenues of engagement:
- Voting: The most fundamental way citizens can influence legislation is through voting. By electing representatives who align with their views, citizens can ensure that their priorities are reflected in the legislative process.
- Contacting Elected Officials: Citizens can directly contact their elected officials through phone calls, emails, and letters to express their views on specific legislation. This can help lawmakers understand the concerns of their constituents and make informed decisions.
- Public Hearings and Testimony: Public hearings provide opportunities for citizens to share their views on proposed legislation. They can provide testimony, submit written statements, and engage in dialogue with lawmakers.
- Joining Advocacy Groups: Citizens can join advocacy groups that align with their interests and participate in their activities. This can involve volunteering, attending meetings, and contributing to campaigns to influence the legislative process.
| Stage | Description | Citizen Engagement |
|---|---|---|
| Issue Identification | Public concerns or problems emerge as potential topics for legislation. | Citizens can raise awareness, share experiences, and advocate for addressing specific issues. |
| Policy Formulation | Lawmakers, experts, and stakeholders develop policy proposals to address the identified issue. | Citizens can provide input, participate in public hearings, and engage in dialogue with policymakers. |
| Legislative Process | Bills are introduced, debated, amended, and voted on in the legislative body. | Citizens can contact their representatives, participate in protests, and advocate for specific legislation. |
| Enactment | A bill is passed by the legislature and signed into law by the executive branch. | Citizens can celebrate victories, continue advocacy, and monitor implementation. |
| Implementation | Government agencies and other stakeholders put the law into practice. | Citizens can monitor implementation, report problems, and advocate for improvements. |
Closure: Which Branch Makes Laws
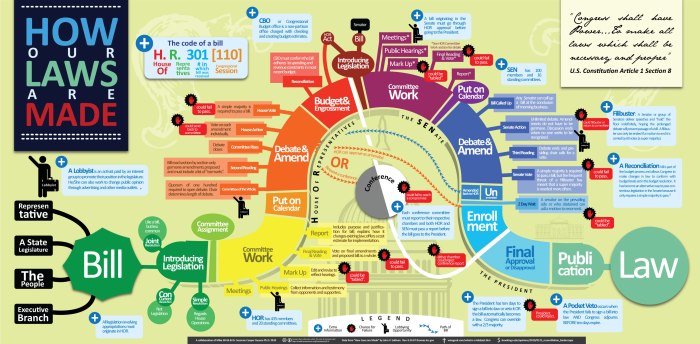
The process of lawmaking in the United States is a testament to the enduring principles of democracy, where the voices of the people are heard, debated, and ultimately reflected in the laws that govern our nation. From the initial spark of an idea to the final stroke of the President’s pen, the journey of a bill is a complex and fascinating process that underscores the importance of checks and balances in our system of government. Understanding this intricate dance of power is crucial for informed citizenship, allowing us to engage in meaningful discussions about the laws that shape our lives.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between a bill and a law?
A bill is a proposed law that is being considered by the legislature. A law is a bill that has been passed by the legislature and signed into law by the President.
How can I get involved in the lawmaking process?
There are many ways to get involved in the lawmaking process, such as contacting your elected officials, attending public hearings, or joining advocacy groups.
What are some examples of landmark court cases that have shaped the meaning of laws?
Some examples of landmark court cases that have shaped the meaning of laws include Marbury v. Madison (1803), Brown v. Board of Education (1954), and Roe v. Wade (1973).




